|
Tizen Native API
10.0
|
To see the full source for this example, click here: eina_inlist_01.c Eina_Inlist basic usage source
As explained before, inline lists mean its nodes pointers are part of same memory block/blob. This is done by using the macro EINA_INLIST inside the data structure that will be used:
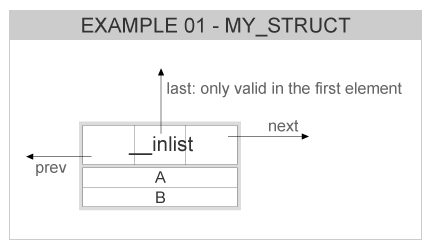
struct my_struct { EINA_INLIST; int a, b; };
The resulting node representing this struct can be exemplified by the following picture:
Let's define a comparison function that will be used later during the sorting of the list:
int sort_cb(const void *d1, const void *d2) { const Eina_Inlist *l1, *l2; const struct my_struct *x1, *x2; l1 = d1; l2 = d2; x1 = EINA_INLIST_CONTAINER_GET(l1, struct my_struct); x2 = EINA_INLIST_CONTAINER_GET(l2, struct my_struct); return x1->a - x2->a; }
The Eina_Inlist can be used exactly the same way as Eina_List when appending, prepending and removing items. But since we already have the node pointers inside the structure, they need to be retrieved with the macro EINA_INLIST_GET :
d = malloc(sizeof(*d)); d->a = 1; d->b = 10; list = eina_inlist_append(NULL, EINA_INLIST_GET(d));
Notice that eina_inlist_append always receives the head of the list as first argument, and its return value should be used as the list pointer (head):
d = malloc(sizeof(*d)); d->a = 2; d->b = 20; list = eina_inlist_append(list, EINA_INLIST_GET(d));
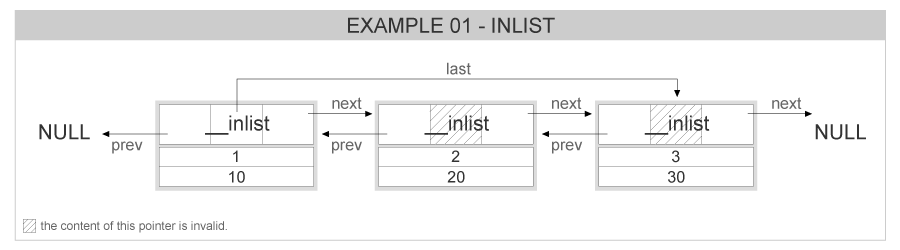
After appending 3 items, the list now should look similar to this:
The macro EINA_INLIST_FOREACH can be used to iterate over the list:
printf("list=%p\n", list); EINA_INLIST_FOREACH(list, cur) printf("\ta=%d, b=%d\n", cur->a, cur->b);
eina_inlist_promote(), eina_inlist_demote(), eina_inlist_append_relative() and similar functions all work in the same way as the Eina_List :
list = eina_inlist_promote(list, EINA_INLIST_GET(d)); d = malloc(sizeof(*d)); d->a = 4; d->b = 40; list = eina_inlist_append_relative(list, EINA_INLIST_GET(d), list); list = eina_inlist_demote(list, EINA_INLIST_GET(d));
Now let's use the sort_cb function declared above to sort our list:
list = eina_inlist_sort(list, sort_cb);
Removing an element from the inlist is also similar to Eina_List :
list = eina_inlist_remove(list, EINA_INLIST_GET(d)); free(d);
Another way of walking through the inlist.
for (itr = list; itr != NULL; itr = itr->next) { cur = EINA_INLIST_CONTAINER_GET(itr, struct my_struct); printf("\ta=%d, b=%d\n", cur->a, cur->b); }
Notice that in the previous piece of code, since we only have the pointers to the inlist nodes, we have to use the EINA_INLIST_CONTAINER_GET macro that will return the pointer to the entire structure. Of course, in this case it is the same as the list pointer, since the EINA_INLIST macro was used in the beginning of the structure.
Now to finish this example, lets delete this list:
while (list) { struct my_struct *aux = EINA_INLIST_CONTAINER_GET(list, struct my_struct); list = eina_inlist_remove(list, list); free(aux); }