Hash table management. Useful for mapping keys to values.
The hash table is useful for when one wants to implement a table that maps keys (usually strings) to data, and have relatively fast access time. The performance is proportional to the load factor of the table (number of elements / number of buckets). See Algorithm for implementation details.
Different implementations exists depending on what kind of key will be used to access the data: strings, integers, pointers, stringshared or your own.
Eina hash tables can copy the keys when using eina_hash_add() or not when using eina_hash_direct_add().
Algorithm
The Eina_Hash is implemented using an array of N "buckets", where each bucket is a pointer to a structure that is the head of a red-black tree. The array can then be indexed by the [hash_of_element mod N]. The hash_of_element is calculated using the hashing function, passed as parameter to the eina_hash_new function. N is the number of buckets (array positions), and is calculated based on the buckets_power_size (argument of eina_hash_new too). The following picture illustrates the basic idea:
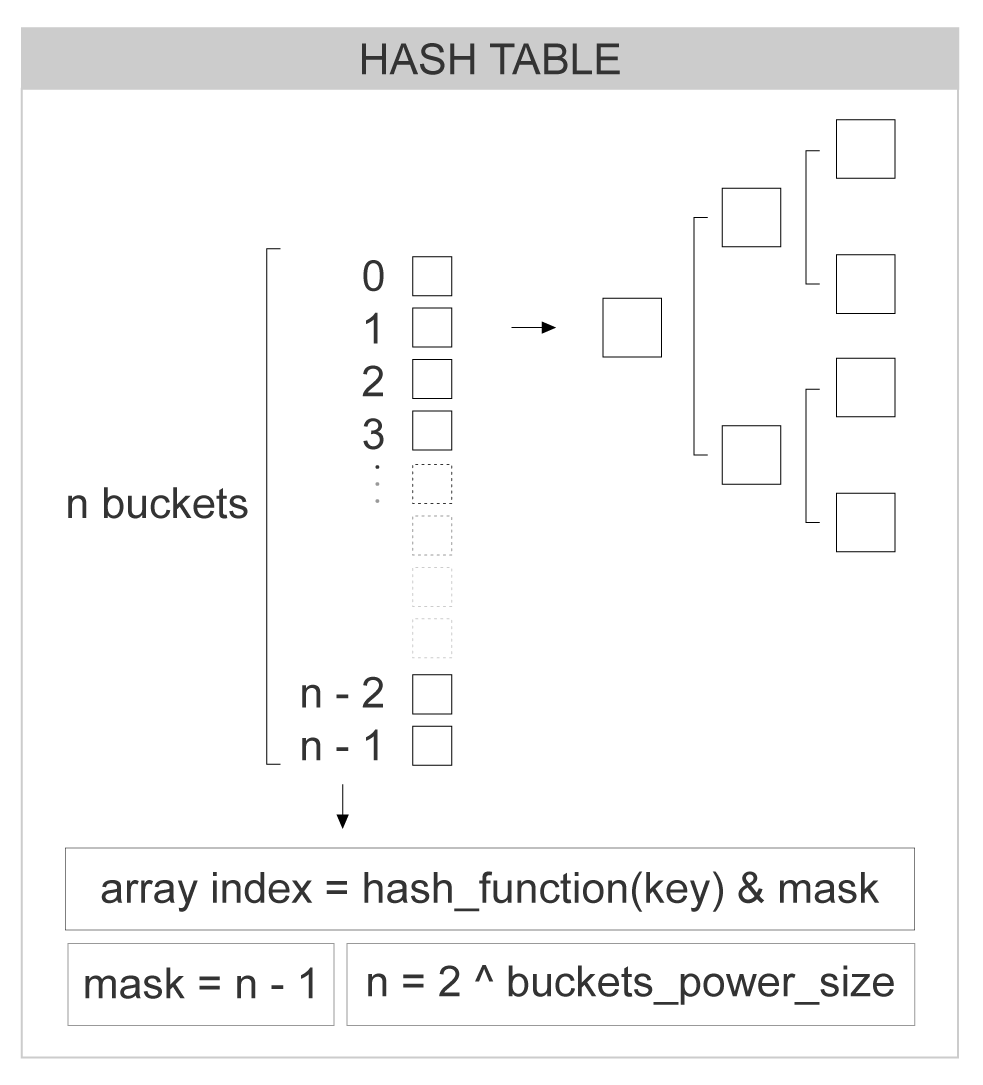
Adding an element to the hash table is made of:
- calculating the hash for that key (using the specified hash function);
- calculate the array position [hash mod N];
- add the element to the rbtree on that position.
The two first steps have constant time, proportional to the hash function being used. Adding the key to the rbtree will be proportional on the number of keys on that bucket.
The average cost of lookup depends on the number of keys per bucket (load factor) of the table, if the distribution of keys is sufficiently uniform.
Performance
As said before, the performance depends on the load factor. So trying to keep the load factor as small as possible will improve the hash table performance. But increasing the buckets_power_size will also increase the memory consumption. The default hash table creation functions already have a good number of buckets, enough for most cases. Particularly for strings, if just a few keys (less than 30) will be added to the hash table, eina_hash_string_small_new should be used, since it will reduce the memory consumption for the buckets, and you still won't have many collisions. However, eina_hash_string_small_new still uses the same hash calculation function that eina_hash_string_superfast_new, which is more complex than eina_hash_string_djb2_new. The latter has a faster hash computation function, but that will imply on a not so good distribution. But if just a few keys are being added, this is not a problem, it will still have not many collisions and be faster to calculate the hash than in a hash created with eina_hash_string_small_new and eina_hash_string_superfast_new.
A simple comparison between them would be:
djb2- faster hash function - 256 buckets (higher memory consumption)string_small- slower hash function but less collisions - 32 buckets (lower memory consumption)string_superfast- slower hash function but less collisions - 256 buckets (higher memory consumption) - not randomized, avoid it on public remote interface.
Basically for a very small number of keys (10 or less), djb2 should be used, or string_small if you have a restriction on memory usage. And for a higher number of keys, string_superfast should be preferred if not used on a public remote interface.
If just stringshared keys are being added, use eina_hash_stringshared_new. If a lot of keys will be added to the hash table (e.g. more than 1000), then it's better to increase the buckets_power_size. See eina_hash_new for more details.
When adding a new key to a hash table, use eina_hash_add or eina_hash_direct_add (the latter if this key is already stored elsewhere). If the key may be already inside the hash table, instead of checking with eina_hash_find and then doing eina_hash_add, one can use just eina_hash_set (this will change the data pointed by this key if it was already present in the table).
Tutorial
These examples show many Eina_Hash functions in action:
- Eina_Hash in action
- Different types of tables
- Different types of hash in use:
- Different add and delete functions
Functions | |
| Eina_Hash * | eina_hash_new (Eina_Key_Length key_length_cb, Eina_Key_Cmp key_cmp_cb, Eina_Key_Hash key_hash_cb, Eina_Free_Cb data_free_cb, int buckets_power_size) |
| Creates a new hash table. | |
| void | eina_hash_free_cb_set (Eina_Hash *hash, Eina_Free_Cb data_free_cb) |
| Redefines the callback that clean the data of a hash. | |
| Eina_Hash * | eina_hash_string_djb2_new (Eina_Free_Cb data_free_cb) |
| Creates a new hash table using the djb2 algorithm. | |
| Eina_Hash * | eina_hash_string_superfast_new (Eina_Free_Cb data_free_cb) |
| Creates a new hash table for use with strings. | |
| Eina_Hash * | eina_hash_string_small_new (Eina_Free_Cb data_free_cb) |
| Creates a new hash table for use with strings with small bucket size. | |
| Eina_Hash * | eina_hash_int32_new (Eina_Free_Cb data_free_cb) |
| Creates a new hash table for use with 32bit integers. | |
| Eina_Hash * | eina_hash_int64_new (Eina_Free_Cb data_free_cb) |
| Creates a new hash table for use with 64bit integers. | |
| Eina_Hash * | eina_hash_pointer_new (Eina_Free_Cb data_free_cb) |
| Creates a new hash table for use with pointers. | |
| Eina_Hash * | eina_hash_stringshared_new (Eina_Free_Cb data_free_cb) |
| Creates a new hash table optimized for stringshared values. | |
| Eina_Bool | eina_hash_add (Eina_Hash *hash, const void *key, const void *data) |
| Adds an entry to the given hash table. | |
| Eina_Bool | eina_hash_direct_add (Eina_Hash *hash, const void *key, const void *data) |
| Adds an entry to the given hash table without duplicating the string. key. | |
| Eina_Bool | eina_hash_del (Eina_Hash *hash, const void *key, const void *data) |
| Removes the entry identified by a key or a data from the given hash table. | |
| void * | eina_hash_find (const Eina_Hash *hash, const void *key) |
| Retrieves a specific entry in the given hash table. | |
| void * | eina_hash_modify (Eina_Hash *hash, const void *key, const void *data) |
| Modifies the entry pointer at the specified key and return the old entry. | |
| void * | eina_hash_set (Eina_Hash *hash, const void *key, const void *data) |
| Modifies the entry pointer at the specified key and return the old entry or add the entry if not found. | |
| Eina_Bool | eina_hash_move (Eina_Hash *hash, const void *old_key, const void *new_key) |
| Changes the key associated with a data without triggering the free callback. | |
| void | eina_hash_free (Eina_Hash *hash) |
| Frees the given hash table resources. | |
| void | eina_hash_free_buckets (Eina_Hash *hash) |
| Frees the given hash table buckets resources. | |
| int | eina_hash_population (const Eina_Hash *hash) |
| Returns the number of entries in the given hash table. | |
| Eina_Bool | eina_hash_add_by_hash (Eina_Hash *hash, const void *key, int key_length, int key_hash, const void *data) |
| Adds an entry to the given hash table. | |
| Eina_Bool | eina_hash_direct_add_by_hash (Eina_Hash *hash, const void *key, int key_length, int key_hash, const void *data) |
| Adds an entry to the given hash table and do not duplicate the string key. | |
| Eina_Bool | eina_hash_del_by_key_hash (Eina_Hash *hash, const void *key, int key_length, int key_hash) |
| Removes the entry identified by a key and a key hash from the given hash table. | |
| Eina_Bool | eina_hash_del_by_key (Eina_Hash *hash, const void *key) |
| Removes the entry identified by a key from the given hash table. | |
| Eina_Bool | eina_hash_del_by_data (Eina_Hash *hash, const void *data) |
| Removes the entry identified by a data from the given hash table. | |
| Eina_Bool | eina_hash_del_by_hash (Eina_Hash *hash, const void *key, int key_length, int key_hash, const void *data) |
| Removes the entry identified by a key and a key hash or a data from the given hash table. | |
| void * | eina_hash_find_by_hash (const Eina_Hash *hash, const void *key, int key_length, int key_hash) |
| Retrieves a specific entry in the given hash table. | |
| void * | eina_hash_modify_by_hash (Eina_Hash *hash, const void *key, int key_length, int key_hash, const void *data) |
| Modifies the entry pointer at the specified key and returns the old entry. | |
| Eina_Iterator * | eina_hash_iterator_key_new (const Eina_Hash *hash) |
| Returns a new iterator associated to hash keys. | |
| Eina_Iterator * | eina_hash_iterator_data_new (const Eina_Hash *hash) |
| Returns a new iterator associated to hash data. | |
| Eina_Iterator * | eina_hash_iterator_tuple_new (const Eina_Hash *hash) |
| Returned a new iterator associated to hash keys and data. | |
| void | eina_hash_foreach (const Eina_Hash *hash, Eina_Hash_Foreach func, const void *fdata) |
| Calls a function on every member stored in the hash table. | |
| void | eina_hash_list_append (Eina_Hash *hash, const void *key, const void *data) |
| Appends data to an Eina_List inside a hash. | |
| void | eina_hash_list_prepend (Eina_Hash *hash, const void *key, const void *data) |
| Prepends data to an Eina_List inside a hash. | |
| void | eina_hash_list_remove (Eina_Hash *hash, const void *key, const void *data) |
| Removes data from an Eina_List inside a hash. | |
| int | eina_hash_superfast (const char *key, int len) |
| Paul Hsieh (http://www.azillionmonkeys.com/qed/hash.html) hash function used by WebCore (http://webkit.org/blog/8/hashtables-part-2/) | |
| static int | eina_hash_djb2 (const char *key, int len) |
| Hash function first reported by Dan Bernstein many years ago in comp.lang.c. | |
| static int | eina_hash_djb2_len (const char *key, int *plen) |
| Hash function first reported by Dan Bernstein many years ago in comp.lang.c. | |
| static int | eina_hash_int32 (const unsigned int *pkey, int len) |
| Hash function from http://web.archive.org/web/20071223173210/http://www.concentric.net/~Ttwang/tech/inthash.htm. | |
| static int | eina_hash_int64 (const unsigned long long int *pkey, int len) |
| Hash function from http://web.archive.org/web/20071223173210/http://www.concentric.net/~Ttwang/tech/inthash.htm. | |
| static int | eina_hash_murmur3 (const char *key, int len) |
| Hash function from http://sites.google.com/site/murmurhash/. | |
| static int | eina_hash_crc (const char *key, int len) |
| Hash function using crc-32 algorithm and and 0xEDB88320 polynomial. | |
Typedefs | |
| typedef struct _Eina_Hash | Eina_Hash |
| typedef struct _Eina_Hash_Tuple | Eina_Hash_Tuple |
| typedef unsigned int(* | Eina_Key_Length )(const void *key) |
| typedef int(* | Eina_Key_Cmp )(const void *key1, int key1_length, const void *key2, int key2_length) |
| typedef int(* | Eina_Key_Hash )(const void *key, int key_length) |
| typedef Eina_Bool(* | Eina_Hash_Foreach )(const Eina_Hash *hash, const void *key, void *data, void *fdata) |
Defines | |
| #define | EINA_KEY_LENGTH(Function) ((Eina_Key_Length)Function) |
| #define | EINA_KEY_CMP(Function) ((Eina_Key_Cmp)Function) |
| #define | EINA_KEY_HASH(Function) ((Eina_Key_Hash)Function) |
Define Documentation
| #define EINA_KEY_CMP | ( | Function | ) | ((Eina_Key_Cmp)Function) |
- Parameters:
-
Function The function used to compare hash key.
- Examples:
- eina_hash_02.c.
| #define EINA_KEY_HASH | ( | Function | ) | ((Eina_Key_Hash)Function) |
- Parameters:
-
Function The function used to hash key.
- Examples:
- eina_hash_02.c.
| #define EINA_KEY_LENGTH | ( | Function | ) | ((Eina_Key_Length)Function) |
- Parameters:
-
Function The function used to calculate length of hash key.
- Examples:
- eina_hash_02.c.
Typedef Documentation
Type for a generic hash table.
Type for a function to iterate over a hash table.
Type for a hash table of key/value pairs.
Type for a function to compare two hash keys.
Type for a function to create a hash key.
Type for a function to determine the length of a hash key.
Function Documentation
| Eina_Bool eina_hash_add | ( | Eina_Hash * | hash, |
| const void * | key, | ||
| const void * | data | ||
| ) |
Adds an entry to the given hash table.
- Parameters:
-
hash The given hash table. Cannot be NULL.key A unique key. Cannot be NULL.data Data to associate with the string given by key. Cannot beNULL.
- Returns:
- EINA_FALSE if an error occurred, EINA_TRUE otherwise.
This function adds key to hash. key is expected to be unique within the hash table. Key uniqueness varies depending on the type of hash: a stringshared Eina_Hash need to have unique pointers (which implies unique strings). All other string hash types require the strings themselves to be unique. Pointer, int32 and int64 hashes need to have these values as unique. Failure to use sufficient uniqueness will result in unexpected results when inserting data pointers accessed with eina_hash_find(), and removed with eina_hash_del(). Key strings are case sensitive. This function returns EINA_FALSE if an error occurred, EINA_TRUE otherwise.
- Since :
- 2.3
- Examples:
- eina_hash_01.c, eina_hash_02.c, eina_hash_03.c, eina_hash_04.c, eina_hash_05.c, eina_hash_06.c, eina_hash_07.c, and eina_hash_08.c.
| Eina_Bool eina_hash_add_by_hash | ( | Eina_Hash * | hash, |
| const void * | key, | ||
| int | key_length, | ||
| int | key_hash, | ||
| const void * | data | ||
| ) |
Adds an entry to the given hash table.
- Parameters:
-
hash The given hash table. Cannot be NULL.key A unique key. Cannot be NULL.key_length The length of the key. key_hash The hash that will always match key. data The data to associate with the string given by the key. Cannot be NULL.
- Returns:
- EINA_FALSE if an error occurred, EINA_TRUE otherwise.
This function adds key to hash. hash, key and data cannot be NULL, in that case EINA_FALSE is returned. key is expected to be a unique within the hash table. Otherwise, one cannot be sure which inserted data pointer will be accessed with eina_hash_find, and removed with eina_hash_del. Do not forget to count '\0' for string when setting the value of key_length. key_hash is expected to always match key. Otherwise, one cannot be sure to find it again with eina_hash_find_by_hash. Key strings are case sensitive. This function returns EINA_FALSE if an error occurred, EINA_TRUE otherwise.
- See also:
- eina_hash_add()
- Since :
- 2.3
- Examples:
- eina_hash_08.c.
| static int eina_hash_crc | ( | const char * | key, |
| int | len | ||
| ) | [static] |
Hash function using crc-32 algorithm and and 0xEDB88320 polynomial.
- Parameters:
-
key The key to hash len The length of the key
- Returns:
- The hash value
| Eina_Bool eina_hash_del | ( | Eina_Hash * | hash, |
| const void * | key, | ||
| const void * | data | ||
| ) |
Removes the entry identified by a key or a data from the given hash table.
- Parameters:
-
hash The given hash table. key The key. data The data pointer to remove if the key is NULL.
- Returns:
- EINA_FALSE if an error occurred, EINA_TRUE otherwise.
This function removes the entry identified by key or data from hash. If a free function was given to the callback on creation, it will be called for the data being deleted. If hash is NULL, the functions returns immediately EINA_FALSE. If key is NULL, then data is used to find the a match to remove, otherwise key is used and data is not required and can be NULL. This function returns EINA_FALSE if an error occurred, EINA_TRUE otherwise.
- Note:
- if you know you already have the key, use eina_hash_del_by_key() or eina_hash_del_by_key_hash(). If you know you don't have the key, use eina_hash_del_by_data() directly.
- Since :
- 2.3
- Examples:
- eina_hash_01.c, eina_hash_03.c, eina_hash_04.c, eina_hash_05.c, eina_hash_06.c, eina_hash_07.c, and eina_hash_08.c.
| Eina_Bool eina_hash_del_by_data | ( | Eina_Hash * | hash, |
| const void * | data | ||
| ) |
Removes the entry identified by a data from the given hash table.
This version is slow since there is no quick access to nodes based on data.
- Parameters:
-
hash The given hash table. Cannot be NULL.data The data value to search and remove. Cannot be NULL.
- Returns:
- EINA_FALSE if an error occurred, EINA_TRUE otherwise. thing goes fine.
This function removes the entry identified by data from hash. If a free function was given to the callback on creation, it will be called for the data being deleted. If hash or data are NULL, the functions returns immediately EINA_FALSE. This function returns EINA_FALSE if an error occurred, EINA_TRUE otherwise.
- Note:
- If you already have the key, use eina_hash_del_by_key() or eina_hash_del_by_key_hash() instead.
- Since :
- 2.3
- Examples:
- eina_hash_08.c.
| Eina_Bool eina_hash_del_by_hash | ( | Eina_Hash * | hash, |
| const void * | key, | ||
| int | key_length, | ||
| int | key_hash, | ||
| const void * | data | ||
| ) |
Removes the entry identified by a key and a key hash or a data from the given hash table.
If key is NULL, then data is used to find a match to remove.
- Parameters:
-
hash The given hash table. Cannot be NULL.key The key. key_length The length of the key. key_hash The hash that always match the key. data The data pointer to remove if the key is NULL.
- Returns:
- EINA_FALSE if an error occurred, EINA_TRUE otherwise.
This function removes the entry identified by key and key_hash, or data, from hash. If a free function was given to the callback on creation, it will be called for the data being deleted. If hash is NULL, the functions returns immediately EINA_FALSE. If key is NULL, then key_length and key_hash are ignored and data is used to find a match to remove, otherwise key and key_hash are used and data is not required and can be NULL. Do not forget to count '\0' for string when setting the value of key_length. This function returns EINA_FALSE if an error occurred, EINA_TRUE otherwise.
- Note:
- If you know you already have the key, use eina_hash_del_by_key_hash(), If you know you don't have the key, use eina_hash_del_by_data() directly.
- Since :
- 2.3
| Eina_Bool eina_hash_del_by_key | ( | Eina_Hash * | hash, |
| const void * | key | ||
| ) |
Removes the entry identified by a key from the given hash table.
This version will calculate key length and hash by using functions provided to hash creation function.
- Parameters:
-
hash The given hash table. Cannot be NULL.key The key. Cannot be NULL.
- Returns:
- EINA_FALSE if an error occurred, EINA_TRUE otherwise.
This function removes the entry identified by key from hash. The key length and hash will be calculated automatically by using function provided to has creation function. If a free function was given to the callback on creation, it will be called for the data being deleted. If hash or key are NULL, the functions returns immediately EINA_FALSE. This function returns EINA_FALSE if an error occurred, EINA_TRUE otherwise.
- Note:
- If you already have the key_hash, use eina_hash_del_by_key_hash() instead.
- If you don't have the key, use eina_hash_del_by_data() instead.
- Since :
- 2.3
- Examples:
- eina_hash_08.c.
| Eina_Bool eina_hash_del_by_key_hash | ( | Eina_Hash * | hash, |
| const void * | key, | ||
| int | key_length, | ||
| int | key_hash | ||
| ) |
Removes the entry identified by a key and a key hash from the given hash table.
- Parameters:
-
hash The given hash table. Cannot be NULL.key The key. Cannot be NULL.key_length The length of the key. key_hash The hash that always match the key.
- Returns:
- EINA_FALSE if an error occurred, EINA_TRUE otherwise.
This function removes the entry identified by key and key_hash from hash. If a free function was given to the callback on creation, it will be called for the data being deleted. Do not forget to count '\0' for string when setting the value of key_length. If hash or key are NULL, the functions returns immediately EINA_FALSE. This function returns EINA_FALSE if an error occurred, EINA_TRUE otherwise.
- Note:
- If you don't have the key_hash, use eina_hash_del_by_key() instead.
- If you don't have the key, use eina_hash_del_by_data() instead.
- Since :
- 2.3
- Examples:
- eina_hash_08.c.
| Eina_Bool eina_hash_direct_add | ( | Eina_Hash * | hash, |
| const void * | key, | ||
| const void * | data | ||
| ) |
Adds an entry to the given hash table without duplicating the string. key.
- Parameters:
-
hash The given hash table. Cannot be NULL.key A unique key. Cannot be NULL.data Data to associate with the string given by key. Cannot beNULL
- Returns:
- EINA_FALSE if an error occurred, EINA_TRUE otherwise.
This function adds key to hash. key is expected to be unique within the hash table. Key uniqueness varies depending on the type of hash: a stringshared Eina_Hash need have unique pointers (which implies unique strings). All other string hash types require the strings themselves to be unique. Pointer, int32 and int64 hashes need to have these values as unique. Failure to use sufficient uniqueness will result in unexpected results when inserting data pointers accessed with eina_hash_find(), and removed with eina_hash_del(). This function does not make a copy of key, so it must be a string constant or stored elsewhere ( in the object being added). Key strings are case sensitive. This function returns EINA_FALSE if an error occurred, EINA_TRUE otherwise.
- Since :
- 2.3
- Examples:
- eina_hash_02.c.
| Eina_Bool eina_hash_direct_add_by_hash | ( | Eina_Hash * | hash, |
| const void * | key, | ||
| int | key_length, | ||
| int | key_hash, | ||
| const void * | data | ||
| ) |
Adds an entry to the given hash table and do not duplicate the string key.
- Parameters:
-
hash The given hash table. Cannot be NULL.key A unique key. Cannot be NULL.key_length Should be the length of key(don't forget to count '\0' for string).key_hash The hash that will always match key. data Data to associate with the string given by key. Cannot beNULL.
- Returns:
- EINA_FALSE if an error occurred, EINA_TRUE otherwise.
This function adds key to hash. hash, key and data can be NULL, in that case EINA_FALSE is returned. key is expected to be unique within the hash table. Otherwise, one cannot be sure which inserted data pointer will be accessed with eina_hash_find, and removed with eina_hash_del. This function does not make a copy of key so it must be a string constant or stored elsewhere (in the object being added). Do not forget to count '\0' for string when setting the value of key_length. key_hash is expected to always match key. Otherwise, one cannot be sure to find it again with eina_hash_find_by_hash. Key strings are case sensitive. This function returns EINA_FALSE if an error occurred, EINA_TRUE otherwise.
- See also:
- eina_hash_direct_add()
- Since :
- 2.3
- Examples:
- eina_hash_08.c.
| static int eina_hash_djb2 | ( | const char * | key, |
| int | len | ||
| ) | [static] |
Hash function first reported by Dan Bernstein many years ago in comp.lang.c.
- Parameters:
-
key The key to hash len The length of the key
- Returns:
- The hash value
| static int eina_hash_djb2_len | ( | const char * | key, |
| int * | plen | ||
| ) | [static] |
Hash function first reported by Dan Bernstein many years ago in comp.lang.c.
- Parameters:
-
key The key to hash plen The length of the key
- Returns:
- The hash value
| void* eina_hash_find | ( | const Eina_Hash * | hash, |
| const void * | key | ||
| ) |
Retrieves a specific entry in the given hash table.
- Parameters:
-
hash The given hash table. key The key of the entry to find.
- Returns:
- The data pointer for the stored entry on success,
NULLotherwise.
This function retrieves the entry associated to key in hash. If hash is NULL, this function returns immediately NULL. This function returns the data pointer on success, NULL otherwise.
- Since :
- 2.3
- Examples:
- eina_hash_01.c, eina_hash_02.c, eina_hash_03.c, eina_hash_04.c, eina_hash_05.c, eina_hash_06.c, and eina_hash_07.c.
| void* eina_hash_find_by_hash | ( | const Eina_Hash * | hash, |
| const void * | key, | ||
| int | key_length, | ||
| int | key_hash | ||
| ) |
Retrieves a specific entry in the given hash table.
- Parameters:
-
hash The given hash table. Cannot be NULL.key The key of the entry to find. key_length The length of the key. key_hash The hash that always match the key
- Returns:
- The data pointer for the stored entry on success,
NULLotherwise.
This function retrieves the entry associated to key of length key_length in hash. key_hash is the hash that always match key. It is ignored if key is NULL. Do not forget to count '\0' for string when setting the value of key_length. If hash is NULL, this function returns immediately NULL. This function returns the data pointer on success, NULL otherwise.
- Since :
- 2.3
- Examples:
- eina_hash_08.c.
| void eina_hash_foreach | ( | const Eina_Hash * | hash, |
| Eina_Hash_Foreach | func, | ||
| const void * | fdata | ||
| ) |
Calls a function on every member stored in the hash table.
- Parameters:
-
hash The hash table whose members will be walked func The function to call on each parameter fdata The data pointer to pass to the function being called
This function goes through every entry in the hash table hash and calls the function func on each member. The function should not modify the hash table contents if it returns 1. If the hash table contents are modified by this function or the function wishes to stop processing it must return 0, otherwise return 1 to keep processing.
Example:
extern Eina_Hash *hash; Eina_Bool hash_fn(const Eina_Hash *hash, const void *key, void *data, void *fdata) { printf("Func data: %s, Hash entry: %s / %p\n", fdata, (const char *)key, data); return 1; } int main(int argc, char **argv) { char *hash_fn_data; hash_fn_data = strdup("Hello World"); eina_hash_foreach(hash, hash_fn, hash_fn_data); free(hash_fn_data); }
- Since :
- 2.3
- Examples:
- eina_hash_01.c, eina_hash_02.c, eina_hash_03.c, eina_hash_04.c, eina_hash_05.c, eina_hash_06.c, and eina_hash_07.c.
| void eina_hash_free | ( | Eina_Hash * | hash | ) |
Frees the given hash table resources.
- Parameters:
-
hash The hash table to be freed.
This function frees up all the memory allocated to storing hash, and call the free callback if it has been passed to the hash table at creation time. If no free callback has been passed, any entries in the table that the program has no more pointers for elsewhere may now be lost, so this should only be called if the program has already freed any allocated data in the hash table or has the pointers for data in the table stored elsewhere as well. If hash is NULL, the function returns immediately.
Example:
extern Eina_Hash *hash; eina_hash_free(hash); hash = NULL;
- Since :
- 2.3
- Examples:
- eina_hash_01.c, eina_hash_02.c, eina_hash_03.c, eina_hash_04.c, eina_hash_05.c, eina_hash_06.c, eina_hash_07.c, and eina_hash_08.c.
| void eina_hash_free_buckets | ( | Eina_Hash * | hash | ) |
Frees the given hash table buckets resources.
- Parameters:
-
hash The hash table whose buckets have to be freed.
This function frees up all the memory allocated to storing the buckets of hash, and calls the free callback on all hash table buckets if it has been passed to the hash table at creation time, then frees the buckets. If no free callback has been passed, no buckets value will be freed. If hash is NULL, the function returns immediately.
- Since :
- 2.3
- Examples:
- eina_hash_01.c, eina_hash_03.c, eina_hash_04.c, eina_hash_05.c, eina_hash_06.c, and eina_hash_07.c.
| void eina_hash_free_cb_set | ( | Eina_Hash * | hash, |
| Eina_Free_Cb | data_free_cb | ||
| ) |
Redefines the callback that clean the data of a hash.
- Parameters:
-
hash The given hash table data_free_cb The function called on each value when the hash table is freed, or when an item is deleted from it. NULLcan be passed as callback to remove an existing callback.
The argument received by data_free_cb will be that data of the item being removed.
- Since (EFL) :
- 1.1
- See also:
- eina_hash_new.
- Since :
- 2.3
| static int eina_hash_int32 | ( | const unsigned int * | pkey, |
| int | len | ||
| ) | [static] |
Hash function from http://web.archive.org/web/20071223173210/http://www.concentric.net/~Ttwang/tech/inthash.htm.
- Parameters:
-
pkey The key to hash len The length of the key
- Returns:
- The hash value
| Eina_Hash* eina_hash_int32_new | ( | Eina_Free_Cb | data_free_cb | ) |
Creates a new hash table for use with 32bit integers.
- Parameters:
-
data_free_cb The function called on each value when the hash table is freed, or when an item is deleted from it. NULLcan be passed as callback.
- Returns:
- The new hash table.
This function creates a new hash table where keys are 32bit integers. When adding or looking up in the hash table, pointers to 32bit integers must be passed. They can be addresses on the stack if you let the eina_hash copy the key. Values can then be looked up with pointers other than the original key pointer that was used to add values. This method is not suitable to match string keys as it would only match the first character. On failure, this function returns NULL.
- Since :
- 2.3
- Examples:
- eina_hash_05.c.
| static int eina_hash_int64 | ( | const unsigned long long int * | pkey, |
| int | len | ||
| ) | [static] |
Hash function from http://web.archive.org/web/20071223173210/http://www.concentric.net/~Ttwang/tech/inthash.htm.
- Parameters:
-
pkey The key to hash len The length of the key
- Returns:
- The hash value
| Eina_Hash* eina_hash_int64_new | ( | Eina_Free_Cb | data_free_cb | ) |
Creates a new hash table for use with 64bit integers.
- Parameters:
-
data_free_cb The function called on each value when the hash table is freed, or when an item is deleted from it. NULLcan be passed as callback.
- Returns:
- The new hash table.
This function creates a new hash table where keys are 64bit integers. When adding or looking up in the hash table, pointers to 64bit integers must be passed. They can be addresses on the stack. Values can then be looked up with pointers other than the original key pointer that was used to add values. This method is not suitable to match string keys as it would only match the first character. On failure, this function returns NULL.
- Since :
- 2.3
- Examples:
- eina_hash_06.c.
| Eina_Iterator* eina_hash_iterator_data_new | ( | const Eina_Hash * | hash | ) |
Returns a new iterator associated to hash data.
- Parameters:
-
hash The hash.
- Returns:
- A new iterator.
This function returns a newly allocated iterator associated to hash. If hash is not populated, this function still returns a valid iterator that will always return false on eina_iterator_next(), thus keeping API sane.
If the memory can not be allocated, NULL is returned. Otherwise, a valid iterator is returned.
- Warning:
- if the hash structure changes then the iterator becomes invalid. That is, if you add or remove items this iterator behavior is undefined and your program may crash.
- Since :
- 2.3
- Examples:
- eina_hash_01.c, eina_hash_03.c, eina_hash_04.c, eina_hash_05.c, eina_hash_06.c, and eina_hash_07.c.
| Eina_Iterator* eina_hash_iterator_key_new | ( | const Eina_Hash * | hash | ) |
Returns a new iterator associated to hash keys.
- Parameters:
-
hash The hash.
- Returns:
- A new iterator.
This function returns a newly allocated iterator associated to hash. If hash is not populated, this function still returns a valid iterator that will always return false on eina_iterator_next(), thus keeping API sane.
If the memory can not be allocated, NULL is returned. Otherwise, a valid iterator is returned.
- Warning:
- if the hash structure changes then the iterator becomes invalid! That is, if you add or remove items this iterator behavior is undefined and your program may crash!
- Since :
- 2.3
- Examples:
- eina_hash_01.c, eina_hash_03.c, eina_hash_04.c, eina_hash_05.c, eina_hash_06.c, and eina_hash_07.c.
| Eina_Iterator* eina_hash_iterator_tuple_new | ( | const Eina_Hash * | hash | ) |
Returned a new iterator associated to hash keys and data.
- Parameters:
-
hash The hash.
- Returns:
- A new iterator.
This function returns a newly allocated iterator associated to hash. If hash is not populated, this function still returns a valid iterator that will always return false on eina_iterator_next(), thus keeping API sane.
If the memory can not be allocated, NULL is returned. Otherwise, a valid iterator is returned.
- Note:
- Iterator data will provide values as Eina_Hash_Tuple that should not be modified!
- Warning:
- if the hash structure changes then the iterator becomes invalid! That is, if you add or remove items this iterator behavior is undefined and your program may crash!
- Since :
- 2.3
- Examples:
- eina_hash_01.c, eina_hash_03.c, eina_hash_04.c, eina_hash_05.c, eina_hash_06.c, and eina_hash_07.c.
| void eina_hash_list_append | ( | Eina_Hash * | hash, |
| const void * | key, | ||
| const void * | data | ||
| ) |
Appends data to an Eina_List inside a hash.
This function is identical to the sequence of calling eina_hash_find(), eina_list_append(), eina_hash_set(), but with one fewer required hash lookup.
- Parameters:
-
hash The hash table key The key associated with the data data The data to append to the list
- Since (EFL) :
- 1.10
- Since :
- 3.0
| void eina_hash_list_prepend | ( | Eina_Hash * | hash, |
| const void * | key, | ||
| const void * | data | ||
| ) |
Prepends data to an Eina_List inside a hash.
This function is identical to the sequence of calling eina_hash_find(), eina_list_prepend(), eina_hash_set(), but with one fewer required hash lookup.
- Parameters:
-
hash The hash table key The key associated with the data data The data to prepend to the list
- Since (EFL) :
- 1.10
- Since :
- 3.0
| void eina_hash_list_remove | ( | Eina_Hash * | hash, |
| const void * | key, | ||
| const void * | data | ||
| ) |
Removes data from an Eina_List inside a hash.
This function is identical to the sequence of calling eina_hash_find(), eina_list_remove(), eina_hash_set(), but with one fewer required hash lookup.
- Parameters:
-
hash The hash table key The key associated with the data data The data to remove from the list
- Since (EFL) :
- 1.10
- Since :
- 3.0
| void* eina_hash_modify | ( | Eina_Hash * | hash, |
| const void * | key, | ||
| const void * | data | ||
| ) |
Modifies the entry pointer at the specified key and return the old entry.
- Parameters:
-
hash The given hash table. key The key of the entry to modify. data The data to replace the old entry.
- Returns:
- The data pointer for the old stored entry on success, or
NULLotherwise.
This function modifies the data of key with data in hash. If no entry is found, nothing is added to hash. On success this function returns the old entry, otherwise it returns NULL.
- Since :
- 2.3
- Examples:
- eina_hash_01.c, eina_hash_03.c, eina_hash_04.c, eina_hash_05.c, eina_hash_06.c, and eina_hash_07.c.
| void* eina_hash_modify_by_hash | ( | Eina_Hash * | hash, |
| const void * | key, | ||
| int | key_length, | ||
| int | key_hash, | ||
| const void * | data | ||
| ) |
Modifies the entry pointer at the specified key and returns the old entry.
- Parameters:
-
hash The given hash table. key The key of the entry to modify. key_length Should be the length of key(don't forget to count '\0' for string).key_hash The hash that always match the key. Ignored if keyisNULL.data The data to replace the old entry, if it exists.
- Returns:
- The data pointer for the old stored entry, or
NULLif not found. If an existing entry is not found, nothing is added to the hash.
- Since :
- 2.3
- Examples:
- eina_hash_08.c.
| Eina_Bool eina_hash_move | ( | Eina_Hash * | hash, |
| const void * | old_key, | ||
| const void * | new_key | ||
| ) |
Changes the key associated with a data without triggering the free callback.
- Parameters:
-
hash The given hash table. old_key The current key associated with the data new_key The new key to associate data with
- Returns:
- EINA_FALSE in any case but success, EINA_TRUE on success.
This function allows for the move of data from one key to another, but does not call the Eina_Free_Cb associated with the hash table when destroying the old key.
- Since :
- 2.3
- Examples:
- eina_hash_01.c, eina_hash_03.c, eina_hash_04.c, eina_hash_05.c, eina_hash_06.c, and eina_hash_07.c.
| static int eina_hash_murmur3 | ( | const char * | key, |
| int | len | ||
| ) | [static] |
Hash function from http://sites.google.com/site/murmurhash/.
- Parameters:
-
key The key to hash len The length of the key
- Returns:
- The hash value
| Eina_Hash* eina_hash_new | ( | Eina_Key_Length | key_length_cb, |
| Eina_Key_Cmp | key_cmp_cb, | ||
| Eina_Key_Hash | key_hash_cb, | ||
| Eina_Free_Cb | data_free_cb, | ||
| int | buckets_power_size | ||
| ) |
Creates a new hash table.
- Parameters:
-
key_length_cb The function called when getting the size of the key. key_cmp_cb The function called when comparing the keys. key_hash_cb The function called when getting the values. data_free_cb The function called on each value when the hash table is freed, or when an item is deleted from it. NULLcan be passed as callback.buckets_power_size The size of the buckets.
- Returns:
- The new hash table.
This function creates a new hash table using user-defined callbacks to manage the hash table. On failure, NULL is returned. If key_cmp_cb or key_hash_cb are NULL, NULL is returned. If buckets_power_size is smaller or equal than 2, or if it is greater or equal than 17, NULL is returned.
The number of buckets created will be 2 ^ buckets_power_size. This means that if buckets_power_size is 5, there will be created 32 buckets. for a buckets_power_size of 8, there will be 256 buckets.
Pre-defined functions are available to create a hash table. See eina_hash_string_djb2_new(), eina_hash_string_superfast_new(), eina_hash_string_small_new(), eina_hash_int32_new(), eina_hash_int64_new(), eina_hash_pointer_new() and eina_hash_stringshared_new().
- Since :
- 2.3
- Examples:
- eina_hash_02.c.
| Eina_Hash* eina_hash_pointer_new | ( | Eina_Free_Cb | data_free_cb | ) |
Creates a new hash table for use with pointers.
- Parameters:
-
data_free_cb The function called on each value when the hash table is freed, or when an item is deleted from it. NULLcan be passed as callback.
- Returns:
- The new hash table.
This function creates a new hash table using the int64/int32 algorithm for table management and dereferenced pointers to compare the keys. Values can then be looked up with pointers other than the original key pointer that was used to add values. This method may appear to be able to match string keys, actually it only matches the first character. On failure, this function returns NULL.
// For a hash that will have only one pointer to each structure extern Eina_Hash *hash; extern void *data; if (!eina_hash_find(hash, &data)) eina_hash_add(hash, &data, data);
- Since :
- 2.3
- Examples:
- eina_hash_07.c.
| int eina_hash_population | ( | const Eina_Hash * | hash | ) |
Returns the number of entries in the given hash table.
- Parameters:
-
hash The given hash table.
- Returns:
- The number of entries in the hash table.
This function returns the number of entries in hash, or 0 on error. If hash is NULL, 0 is returned.
- Since :
- 2.3
- Examples:
- eina_hash_01.c, eina_hash_03.c, eina_hash_04.c, eina_hash_05.c, eina_hash_06.c, and eina_hash_07.c.
| void* eina_hash_set | ( | Eina_Hash * | hash, |
| const void * | key, | ||
| const void * | data | ||
| ) |
Modifies the entry pointer at the specified key and return the old entry or add the entry if not found.
- Parameters:
-
hash The given hash table. key The key of the entry to modify. data The data to replace the old entry
- Returns:
- The data pointer for the old stored entry, or
NULLotherwise.
This function modifies the data of key with data in hash. If no entry is found, data is added to hash with the key key. On success this function returns the old entry, otherwise it returns NULL.
- Since :
- 2.3
- Examples:
- eina_hash_01.c, eina_hash_03.c, eina_hash_04.c, eina_hash_05.c, eina_hash_06.c, and eina_hash_07.c.
| Eina_Hash* eina_hash_string_djb2_new | ( | Eina_Free_Cb | data_free_cb | ) |
Creates a new hash table using the djb2 algorithm.
- Parameters:
-
data_free_cb The function called on each value when the hash table is freed, or when an item is deleted from it. NULLcan be passed as callback.
- Returns:
- The new hash table.
This function creates a new hash table using the djb2 algorithm for table management and strcmp() to compare the keys. Values can then be looked up with pointers other than the original key pointer that was used to add values. On failure, this function returns NULL.
- Since :
- 2.3
- Examples:
- eina_hash_04.c.
| Eina_Hash* eina_hash_string_small_new | ( | Eina_Free_Cb | data_free_cb | ) |
Creates a new hash table for use with strings with small bucket size.
- Parameters:
-
data_free_cb The function called on each value when the hash table is freed, or when an item is deleted from it. NULLcan be passed as callback.
- Returns:
- The new hash table.
This function creates a new hash table using the superfast algorithm for table management and strcmp() to compare the keys, but with a smaller bucket size (compared to eina_hash_string_superfast_new()) which will minimize the memory used by the returned hash table. Values can then be looked up with pointers other than the original key pointer that was used to add values. On failure, this function returns NULL.
- Since :
- 2.3
- Examples:
- eina_hash_03.c.
| Eina_Hash* eina_hash_string_superfast_new | ( | Eina_Free_Cb | data_free_cb | ) |
Creates a new hash table for use with strings.
- Parameters:
-
data_free_cb The function called on each value when the hash table is freed, or when an item is deleted from it. NULLcan be passed as callback.
- Returns:
- The new hash table.
This function creates a new hash table using the superfast algorithm for table management and strcmp() to compare the keys. Values can then be looked up with pointers other than the original key pointer that was used to add values. On failure, this function returns NULL.
NOTE: don't use this kind of hash when their is a possibility to remotely request and push data in it. This hash is subject to denial of service.
- Since :
- 2.3
- Examples:
- eina_hash_01.c, and eina_hash_08.c.
| Eina_Hash* eina_hash_stringshared_new | ( | Eina_Free_Cb | data_free_cb | ) |
Creates a new hash table optimized for stringshared values.
- Parameters:
-
data_free_cb The function called on each value when the hash table is freed, or when an item is deleted from it. NULLcan be passed as callback.
- Returns:
- The new hash table.
This function creates a new hash table optimized for stringshared values. Values CAN NOT be looked up with pointers not equal to the original key pointer that was used to add a value. On failure, this function returns NULL.
Excerpt of code that will NOT work with this type of hash:
extern Eina_Hash *hash; extern const char *value; const char *a = eina_stringshare_add("key"); eina_hash_add(hash, a, value); eina_hash_find(hash, "key");
- Since :
- 2.3
- Examples:
- eina_hash_02.c.
| int eina_hash_superfast | ( | const char * | key, |
| int | len | ||
| ) |
Paul Hsieh (http://www.azillionmonkeys.com/qed/hash.html) hash function used by WebCore (http://webkit.org/blog/8/hashtables-part-2/)
- Parameters:
-
key The key to hash len The length of the key
- Returns:
- The hash value
- Since :
- 2.3
- Examples:
- eina_hash_02.c, and eina_hash_08.c.