These functions allow you to store a single copy of a string, and use in multiple places throughout your program.
This is a method to reduce the number of duplicated strings kept in memory. It's pretty common for the same strings to be dynamically allocated repeatedly between applications and libraries, especially in circumstances where you could have multiple copies of a structure that allocates the string. So rather than duplicating and freeing these strings, you request a read-only pointer to an existing string and only incur the overhead of a hash lookup.
It sounds like micro-optimizing, but profiling has shown this can have a significant impact as you scale the number of copies up. It improves string creation/destruction speed, reduces memory use and decreases memory fragmentation, so a win all-around.
Using eina stringshares usually boils down to:
const char *str = eina_stringshare_add("My string"); ... //Use str ... eina_stringshare_del(str);
- Note:
- It's very important to note that string shares are
const, changing them will result in undefined behavior. - eina_stringshare_del() doesn't guarantee the string share will be freed, it releases a reference to it, but if other references to it still exist the string share will live until those are released.
The following diagram gives an idea of what happens as you create strings with eina_stringshare_add():
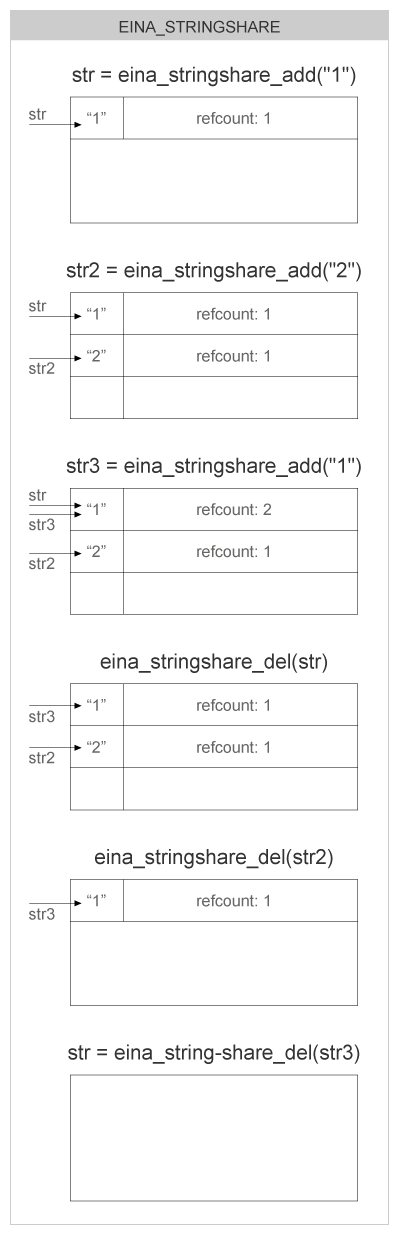
For more information, see this example.
Functions | |
| Eina_Stringshare * | eina_stringshare_add_length (const char *str, unsigned int slen) |
| Retrieves an instance of a string with a specific size for use in a program. | |
| Eina_Stringshare * | eina_stringshare_add (const char *str) |
| Retrieves an instance of a string for use in a program. | |
| Eina_Stringshare * | eina_stringshare_printf (const char *fmt,...) |
| Retrieves an instance of a string for use in a program from a format string. | |
| Eina_Stringshare * | eina_stringshare_vprintf (const char *fmt, va_list args) |
| Retrieves an instance of a string for use in a program from a format string. | |
| Eina_Stringshare * | eina_stringshare_nprintf (unsigned int len, const char *fmt,...) |
| Retrieves an instance of a string for use in a program from a format string with size limitation. | |
| Eina_Stringshare * | eina_stringshare_ref (Eina_Stringshare *str) |
| void | eina_stringshare_del (Eina_Stringshare *str) |
| Notes that the given string has lost an instance. | |
| int | eina_stringshare_strlen (Eina_Stringshare *str) |
| Notes that the given string must be shared. | |
| void | eina_stringshare_dump (void) |
| Dumps the contents of the share_common. | |
| Eina_Tmpstr * | eina_tmpstr_add (const char *str) |
| Adds a new temporary string based on the input string. | |
| Eina_Tmpstr * | eina_tmpstr_add_length (const char *str, size_t length) |
| Adds a new temporary string based on the input string and length. | |
| size_t | eina_tmpstr_strlen (Eina_Tmpstr *tmpstr) |
| **Deprecated** Return the length of a temporary string including the '\0'. | |
| size_t | eina_tmpstr_len (Eina_Tmpstr *tmpstr) |
| Returns the length of a temporary string. | |
| void | eina_tmpstr_del (Eina_Tmpstr *tmpstr) |
| Deletes the temporary string if it is one, or ignore it if it is not. | |
| Eina_Tmpstr * | eina_tmpstr_manage_new (char *str) |
| Adds a new temporary string using the passed string. The passed string is used directly as the buffer. The passed string must be malloced. | |
| Eina_Tmpstr * | eina_tmpstr_manage_new_length (char *str, size_t length) |
| Adds a new temporary string using the passed string. The passed string is used directly as the buffer. The passed string must be malloced. | |
Typedefs | |
| typedef const char | Eina_Stringshare |
| typedef const char | Eina_Tmpstr |
Typedef Documentation
"Eina_Stringshare *" is interchangeable with "const char *" but still a good visual hint for the purpose. Maybe in the far far future we'll even add strict type checking.
- Since (EFL) :
- 1.2.0
Interchangeable with "const char *" but still a good visual hint for the purpose. This indicates the string is temporary and should be freed after use.
- Since (EFL) :
- 1.8.0
Function Documentation
| Eina_Stringshare* eina_stringshare_add | ( | const char * | str | ) |
Retrieves an instance of a string for use in a program.
- Parameters:
-
[in] str The NULL-terminated string to retrieve an instance of.
- Returns:
- A pointer to an instance of the string on success,
NULLon failure.
This function retrieves an instance of str. If str is NULL, then NULL is returned. If str is already stored, it is just returned and its reference counter is increased. Otherwise a duplicated string of str is returned.
The string str must be NULL terminated ('\0') and its full length will be used. To use part of the string or non-null terminated, use eina_stringshare_add_length() instead.
- See also:
- eina_stringshare_add_length()
- Since :
- 2.3
- Examples:
- eina_hash_02.c, eina_list_04.c, eina_stringshare_01.c, and gengrid_example.c.
| Eina_Stringshare* eina_stringshare_add_length | ( | const char * | str, |
| unsigned int | slen | ||
| ) |
Retrieves an instance of a string with a specific size for use in a program.
- Parameters:
-
[in] str The string to retrieve an instance of. [in] slen The string size (<= strlen(str)).
- Returns:
- A pointer to an instance of the string on success,
NULLon failure.
This function retrieves an instance of str. If str is NULL, then NULL is returned. If str is already stored, it is just returned and its reference counter is increased. Otherwise a duplicated string of str is returned.
This function does not check string size, but uses the exact given size. This can be used to share_common part of a larger buffer or substring.
- See also:
- eina_share_common_add()
- Since :
- 2.3
- Examples:
- eina_stringshare_01.c.
| void eina_stringshare_del | ( | Eina_Stringshare * | str | ) |
Notes that the given string has lost an instance.
- Parameters:
-
[in,out] str String the given string.
This function decreases the reference counter associated to str if it exists. If that counter reaches 0, the memory associated to str is freed. If str is NULL, the function returns immediately.
- Note:
- If the given pointer is not shared, bad things will happen, likely a segmentation fault.
- Since :
- 2.3
| void eina_stringshare_dump | ( | void | ) |
Dumps the contents of the share_common.
This function dumps all strings in the share_common to stdout with a DDD: prefix per line and a memory usage summary.
- Since :
- 2.3
| Eina_Stringshare* eina_stringshare_nprintf | ( | unsigned int | len, |
| const char * | fmt, | ||
| ... | |||
| ) |
Retrieves an instance of a string for use in a program from a format string with size limitation.
- Parameters:
-
[in] len The length of the format string to use [in] fmt The format string to retrieve an instance of.
- Returns:
- A pointer to an instance of the string on success,
NULLon failure.
This function retrieves an instance of fmt limited by len. If fmt is NULL or len is < 1, then NULL is returned. If the resulting string is already stored, it is returned and its reference counter is increased. Otherwise a duplicated string is returned.
len length of the format string will be used. To use the entire format string, use eina_stringshare_printf() instead.
- See also:
- eina_stringshare_printf()
- Since :
- 2.3
- Examples:
- eina_stringshare_01.c.
| Eina_Stringshare* eina_stringshare_printf | ( | const char * | fmt, |
| ... | |||
| ) |
Retrieves an instance of a string for use in a program from a format string.
- Parameters:
-
[in] fmt The NULL-terminated format string to retrieve an instance of.
- Returns:
- A pointer to an instance of the string on success,
NULLon failure.
This function retrieves an instance of fmt. If fmt is NULL, then NULL is returned. If fmt is already stored, it is just returned and its reference counter is increased. Otherwise a duplicated string is returned.
The format string fmt must be NULL-terminated ('\0') and its full length will be used. To use part of the format string or non-null terminated, use eina_stringshare_nprintf() instead.
- See also:
- eina_stringshare_nprintf()
- Since :
- 2.3
- Examples:
- eina_stringshare_01.c.
Increment references of the given shared string.
- Parameters:
-
[in,out] str The shared string.
- Returns:
- A pointer to an instance of the string on success,
NULLon failure.
This is similar to eina_share_common_add(), but it's faster since it will avoid lookups if possible, but on the down side it requires the parameter to be shared string. In other words, it must be the return of a previous call to one of the stringshare functions.
There is no unref since this is the work of eina_share_common_del().
- Since :
- 2.3
- Examples:
- eina_stringshare_01.c, and web_example_02.c.
| int eina_stringshare_strlen | ( | Eina_Stringshare * | str | ) |
Notes that the given string must be shared.
- Parameters:
-
[in] str The shared string to know the length. It is safe to give NULL, in that case0is returned.
- Returns:
- The length of a shared string.
This function is a cheap way to known the length of a shared string.
- Note:
- If the given pointer is not shared, bad things will happen, likely a segmentation fault. If in doubt, try strlen().
- Since :
- 2.3
- Examples:
- ecore_thread_example.c, and eina_stringshare_01.c.
| Eina_Stringshare* eina_stringshare_vprintf | ( | const char * | fmt, |
| va_list | args | ||
| ) |
Retrieves an instance of a string for use in a program from a format string.
- Parameters:
-
[in] fmt The NULL-terminated format string to retrieve an instance of. [in] args The va_args for fmt
- Returns:
- A pointer to an instance of the string on success,
NULLon failure.
This function retrieves an instance of fmt with args. If fmt is NULL, then NULL is returned. If fmt with args is already stored, it is just returned and its reference counter is increased. Otherwise a duplicated string is returned.
The format string fmt must be NULL-terminated ('\0') and its full length will be used. To use part of the format string or non-null terminated, use eina_stringshare_nprintf() instead.
- See also:
- eina_stringshare_nprintf()
- Since :
- 2.3
| Eina_Tmpstr* eina_tmpstr_add | ( | const char * | str | ) |
Adds a new temporary string based on the input string.
- Parameters:
-
[in] str This is the input string that is copied into the temp string.
- Returns:
- A pointer to the tmp string that is a standard C string.
When you add a temporary string (tmpstr) it is expected to have a very short lifespan, and at any one time only a few of these are intended to exist. This is not intended for longer term storage of strings. The intended use is the ability to safely pass strings as return values from functions directly into parameters of new functions and then have the string be cleaned up automatically by the caller.
If str is NULL, or no memory space exists to store the tmpstr, then NULL will be returned, otherwise a valid string pointer will be returned that you can treat as any other C string (e.g. strdup(tmpstr) or printf("%s\n", tmpstr) etc.). This string should be considered read-only and immutable, and when you are done with the string you should delete it with eina_tmpstr_del().
Example usage:
Eina_Tmpstr *my_homedir(void) { return eina_tmpstr_add(eina_environment_home_get()); } void my_rmfile(Eina_Tmpstr *str) { if (!str) return; unlink(str); eina_tmpstr_del(str); } my_rmfile(my_homedir()); my_rmfile("/tmp/file");
- Since (EFL) :
- 1.8.0
- Since :
- 2.3
| Eina_Tmpstr* eina_tmpstr_add_length | ( | const char * | str, |
| size_t | length | ||
| ) |
Adds a new temporary string based on the input string and length.
- Parameters:
-
[in] str This is the input string that is copied into the temp string. [in] length This is the maximum length and the allocated length of the temp string.
- Returns:
- A pointer to the tmp string that is a standard C string.
When you add a temporary string (tmpstr) it is expected to have a very short lifespan, and at any one time only a few of these are intended to exist. This is not intended for longer term storage of strings. The intended use is the ability to safely pass strings as return values from functions directly into parameters of new functions and then have the string be cleaned up automatically by the caller.
If str is NULL, or no memory space exists to store the tmpstr, then NULL will be returned, otherwise a valid string pointer will be returned that you can treat as any other C string (e.g. strdup(tmpstr) or printf("%s\n", tmpstr) etc.). This string should be considered read-only and immutable, and when you are done with the string you should delete it with eina_tmpstr_del().
- Note:
- If the length is greater than the actual string, but still '\0' terminated, there won't be any crash and the string will be correct, but eina_tmpstr_len will return an erroneous length. So if you want to have the correct length always call eina_tmpstr_add_length with length == strlen(str).
- See also:
- eina_tmpstr_del()
- eina_tmpstr_add()
- Since (EFL) :
- 1.8.0
- Since :
- 2.3
| void eina_tmpstr_del | ( | Eina_Tmpstr * | tmpstr | ) |
Deletes the temporary string if it is one, or ignore it if it is not.
- Parameters:
-
[in] tmpstr This is any C string pointer, but if it is a tmp string it is freed.
This will delete the given temporary string tmpstr if it is a valid temporary string, or otherwise it will ignore it and do nothing so this can be used safely with non-temporary strings.
- See also:
- eina_tmpstr_add()
- Since (EFL) :
- 1.8.0
- Since :
- 2.3
| size_t eina_tmpstr_len | ( | Eina_Tmpstr * | tmpstr | ) |
Returns the length of a temporary string.
- Parameters:
-
[in] tmpstr This is any C string pointer, but if it is a tmp string it will return the length faster.
- Returns:
- The length of the string.
- Since (EFL) :
- 1.14.0
- Since :
- 3.0f(2.3.1)
| Eina_Tmpstr* eina_tmpstr_manage_new | ( | char * | str | ) |
Adds a new temporary string using the passed string. The passed string is used directly as the buffer. The passed string must be malloced.
- Parameters:
-
[in] str The input string to manage.
- Returns:
- A pointer to the tmp string that is a standard C string.
This function creates a new temporary string. On error, NULL is returned. To free the resources, use eina_tmpstr_del().
- See also:
- eina_tmpstr_del()
- Since (EFL) :
- 1.17.0
| Eina_Tmpstr* eina_tmpstr_manage_new_length | ( | char * | str, |
| size_t | length | ||
| ) |
Adds a new temporary string using the passed string. The passed string is used directly as the buffer. The passed string must be malloced.
- Parameters:
-
[in] str The input string to manage. [in] length The length of the string.
- Returns:
- A pointer to the tmp string that is a standard C string.
This function creates a new temporary string. On error, NULL is returned. To free the resources, use eina_tmpstr_del().
- Since (EFL) :
- 1.17.0
| size_t eina_tmpstr_strlen | ( | Eina_Tmpstr * | tmpstr | ) |
**Deprecated** Return the length of a temporary string including the '\0'.
- Parameters:
-
tmpstr This is any C string pointer, but if it is a tmp string it will return the length faster.
- Returns:
- The length of the string including the '\0'
- See also:
- eina_tmpstr_len()
- Since (EFL) :
- 1.8.0
- Since :
- 2.3