|
Tizen Native API
|
Functions | |
| void | evas_object_freeze_events_set (Evas_Object *obj, Eina_Bool freeze) |
| Set whether an Evas object is to freeze (discard) events. | |
| Eina_Bool | evas_object_freeze_events_get (const Evas_Object *obj) |
| Determine whether an object is set to freeze (discard) events. | |
| void | evas_object_repeat_events_set (Evas_Object *obj, Eina_Bool repeat) |
| Set whether an Evas object is to repeat events. | |
| Eina_Bool | evas_object_repeat_events_get (const Evas_Object *obj) |
| Determine whether an object is set to repeat events. | |
| void | evas_object_propagate_events_set (Evas_Object *obj, Eina_Bool propagate) |
| Set whether events on a smart object's member should get propagated up to its parent. | |
| Eina_Bool | evas_object_propagate_events_get (const Evas_Object *obj) |
| Retrieve whether an Evas object is set to propagate events. | |
| void | evas_object_pass_events_set (Evas_Object *obj, Eina_Bool pass) |
| Set whether an Evas object is to pass (ignore) events. | |
| Eina_Bool | evas_object_pass_events_get (const Evas_Object *obj) |
| Determine whether an object is set to pass (ignore) events. | |
| void | evas_object_event_callback_add (Evas_Object *obj, Evas_Callback_Type type, Evas_Object_Event_Cb func, const void *data) |
| Add (register) a callback function to a given Evas object event. | |
| void | evas_object_event_callback_priority_add (Evas_Object *obj, Evas_Callback_Type type, Evas_Callback_Priority priority, Evas_Object_Event_Cb func, const void *data) |
| Add (register) a callback function to a given Evas object event with a non-default priority set. Except for the priority field, it's exactly the same as evas_object_event_callback_add. | |
| void * | evas_object_event_callback_del (Evas_Object *obj, Evas_Callback_Type type, Evas_Object_Event_Cb func) |
| Delete a callback function from an object. | |
| void * | evas_object_event_callback_del_full (Evas_Object *obj, Evas_Callback_Type type, Evas_Object_Event_Cb func, const void *data) |
| Delete (unregister) a callback function registered to a given Evas object event. | |
Typedefs | |
| typedef void(* | Evas_Object_Event_Cb )(void *data, Evas *e, Evas_Object *obj, void *event_info) |
| Evas object event callback function signature. | |
Objects generate events when they are moved, resized, when their visibility change, when they are deleted and so on. These methods allow one to be notified about and to handle such events.
Objects also generate events on input (keyboard and mouse), if they accept them (are visible, focused, etc).
For each of those events, Evas provides a way for one to register callback functions to be issued just after they happen.
The following figure illustrates some Evas (event) callbacks:
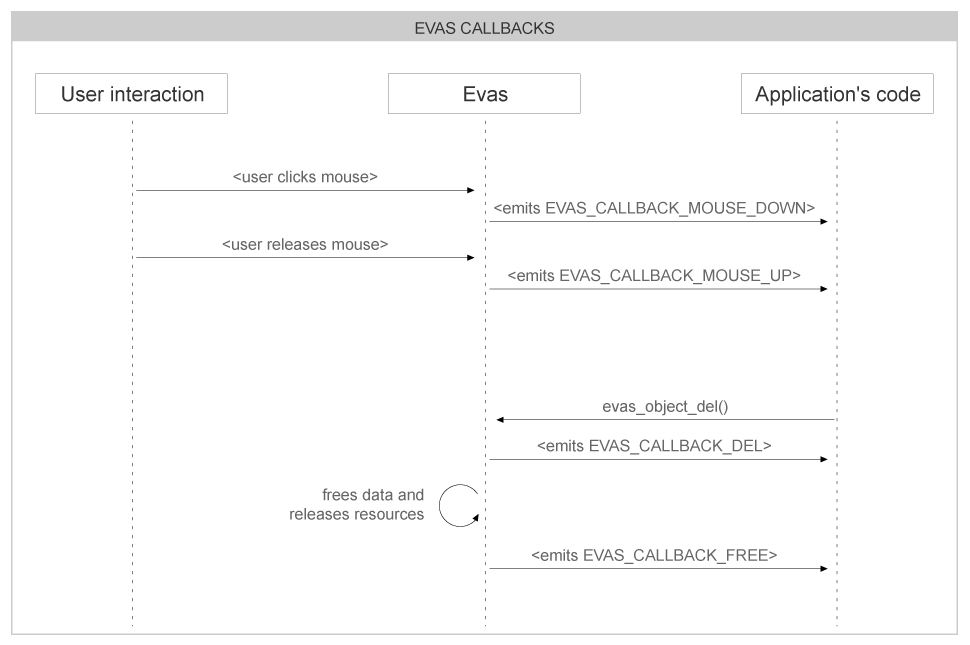
These events have their values in the Evas_Callback_Type enumeration, which has also ones happening on the canvas level (see Canvas Events ).
Examples on this group of functions can be found Evas object stacking functions (and some event handling) here and Evas events (canvas and object ones) and some canvas operations example here.
Typedef Documentation
| typedef void(* Evas_Object_Event_Cb)(void *data, Evas *e, Evas_Object *obj, void *event_info) |
Evas object event callback function signature.
- Since :
- 2.3
Function Documentation
| void evas_object_event_callback_add | ( | Evas_Object * | obj, |
| Evas_Callback_Type | type, | ||
| Evas_Object_Event_Cb | func, | ||
| const void * | data | ||
| ) |
Add (register) a callback function to a given Evas object event.
- Since :
- 2.3
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj Object to attach a callback to [in] type The type of event that will trigger the callback [in] func The function to be called when the event is triggered [in] data The data pointer to be passed to func
- Remarks:
- This function adds a function callback to an object when the event of type
typeoccurs on objectobj. The function isfunc. - In the event of a memory allocation error during addition of the callback to the object, Evas Alloc Error function should be used to determine the nature of the error, if any, and the program should sensibly try and recover.
-
A callback function must have the Evas_Object_Event_Cb prototype definition. The first parameter (
data) in this definition will have the same value passed to evas_object_event_callback_add() as thedataparameter, at runtime. The second parametereis the canvas pointer on which the event occurred. The third parameter is a pointer to the object on which event occurred. Finally, the fourth parameterevent_infois a pointer to a data structure that may or may not be passed to the callback, depending on the event type that triggered the callback. This is so because some events don't carry extra context with them, but others do. -
The event type
typeto trigger the function may be one of EVAS_CALLBACK_MOUSE_IN, EVAS_CALLBACK_MOUSE_OUT, EVAS_CALLBACK_MOUSE_DOWN, EVAS_CALLBACK_MOUSE_UP, EVAS_CALLBACK_MOUSE_MOVE, EVAS_CALLBACK_MOUSE_WHEEL, EVAS_CALLBACK_MULTI_DOWN, EVAS_CALLBACK_MULTI_UP, EVAS_CALLBACK_AXIS_UPDATE, EVAS_CALLBACK_MULTI_MOVE, EVAS_CALLBACK_FREE, EVAS_CALLBACK_KEY_DOWN, EVAS_CALLBACK_KEY_UP, EVAS_CALLBACK_FOCUS_IN, EVAS_CALLBACK_FOCUS_OUT, EVAS_CALLBACK_SHOW, EVAS_CALLBACK_HIDE, EVAS_CALLBACK_MOVE, EVAS_CALLBACK_RESIZE, EVAS_CALLBACK_RESTACK, EVAS_CALLBACK_DEL, EVAS_CALLBACK_HOLD, EVAS_CALLBACK_CHANGED_SIZE_HINTS, EVAS_CALLBACK_IMAGE_PRELOADED or EVAS_CALLBACK_IMAGE_UNLOADED. -
This determines the kind of event that will trigger the callback. What follows is a list explaining better the nature of each type of event, along with their associated
event_infopointers:
- EVAS_CALLBACK_MOUSE_IN:
event_infois a pointer to an Evas_Event_Mouse_In struct
This event is triggered when the mouse pointer enters the area (not shaded by other objects) of the objectobj. This may occur by the mouse pointer being moved by evas_event_feed_mouse_move() calls, or by the object being shown, raised, moved, resized, or other objects being moved out of the way, hidden or lowered, whatever may cause the mouse pointer to get on top ofobj, having been on top of another object previously.
- EVAS_CALLBACK_MOUSE_OUT:
event_infois a pointer to an Evas_Event_Mouse_Out struct
This event is triggered exactly like EVAS_CALLBACK_MOUSE_IN is, but it occurs when the mouse pointer exits an object's area. Note that no mouse out events will be reported if the mouse pointer is implicitly grabbed to an object (mouse buttons are down, having been pressed while the pointer was over that object). In these cases, mouse out events will be reported once all buttons are released, if the mouse pointer has left the object's area. The indirect ways of taking off the mouse pointer from an object, like cited above, for EVAS_CALLBACK_MOUSE_IN, also apply here, naturally.
- EVAS_CALLBACK_MOUSE_DOWN:
event_infois a pointer to an Evas_Event_Mouse_Down struct
This event is triggered by a mouse button being pressed while the mouse pointer is over an object. If the pointer mode for Evas is EVAS_OBJECT_POINTER_MODE_AUTOGRAB (default), this causes this object to passively grab the mouse until all mouse buttons have been released: all future mouse events will be reported to only this object until no buttons are down. That includes mouse move events, mouse in and mouse out events, and further button presses. When all buttons are released, event propagation will occur as normal (see Evas_Object_Pointer_Mode).
- EVAS_CALLBACK_MOUSE_UP:
event_infois a pointer to an Evas_Event_Mouse_Up struct
This event is triggered by a mouse button being released while the mouse pointer is over an object's area (or when passively grabbed to an object).
- EVAS_CALLBACK_MOUSE_MOVE:
event_infois a pointer to an Evas_Event_Mouse_Move struct
This event is triggered by the mouse pointer being moved while over an object's area (or while passively grabbed to an object).
- EVAS_CALLBACK_MOUSE_WHEEL:
event_infois a pointer to an Evas_Event_Mouse_Wheel struct
This event is triggered by the mouse wheel being rolled while the mouse pointer is over an object (or passively grabbed to an object).
- EVAS_CALLBACK_MULTI_DOWN:
event_infois a pointer to an Evas_Event_Multi_Down struct
- EVAS_CALLBACK_MULTI_UP:
event_infois a pointer to an Evas_Event_Multi_Up struct
- EVAS_CALLBACK_MULTI_MOVE:
event_infois a pointer to an Evas_Event_Multi_Move struct
- EVAS_CALLBACK_AXIS_UPDATE:
event_infois a pointer to an Evas_Event_Axis_Update struct
- EVAS_CALLBACK_FREE:
event_infoisNULL
This event is triggered just before Evas is about to free all memory used by an object and remove all references to it. This is useful for programs to use if they attached data to an object and want to free it when the object is deleted. The object is still valid when this callback is called, but after it returns, there is no guarantee on the object's validity.
- EVAS_CALLBACK_KEY_DOWN:
event_infois a pointer to an Evas_Event_Key_Down struct
This callback is called when a key is pressed and the focus is on the object, or a key has been grabbed to a particular object which wants to intercept the key press regardless of what object has the focus.
- EVAS_CALLBACK_KEY_UP:
event_infois a pointer to an Evas_Event_Key_Up struct
This callback is called when a key is released and the focus is on the object, or a key has been grabbed to a particular object which wants to intercept the key release regardless of what object has the focus.
- EVAS_CALLBACK_FOCUS_IN:
event_infoisNULL
This event is called when an object gains the focus. When it is called the object has already gained the focus.
- EVAS_CALLBACK_FOCUS_OUT:
event_infoisNULL
This event is triggered when an object loses the focus. When it is called the object has already lost the focus.
- EVAS_CALLBACK_SHOW:
event_infoisNULL
This event is triggered by the object being shown by evas_object_show().
- EVAS_CALLBACK_HIDE:
event_infoisNULL
This event is triggered by an object being hidden by evas_object_hide().
- EVAS_CALLBACK_MOVE:
event_infoisNULL
This event is triggered by an object being moved. evas_object_move() can trigger this, as can any object-specific manipulations that would mean the object's origin could move.
- EVAS_CALLBACK_RESIZE:
event_infoisNULL
This event is triggered by an object being resized. Resizes can be triggered by evas_object_resize() or by any object-specific calls that may cause the object to resize.
- EVAS_CALLBACK_RESTACK:
event_infoisNULL
This event is triggered by an object being re-stacked. Stacking changes can be triggered by evas_object_stack_below()/evas_object_stack_above() and others.
- EVAS_CALLBACK_DEL:
event_infoisNULL.
- EVAS_CALLBACK_HOLD:
event_infois a pointer to an Evas_Event_Hold struct
- EVAS_CALLBACK_CHANGED_SIZE_HINTS:
event_infoisNULL.
- EVAS_CALLBACK_IMAGE_PRELOADED:
event_infoisNULL.
- EVAS_CALLBACK_IMAGE_UNLOADED:
event_infoisNULL.
- Remarks:
- Be careful not to add the same callback multiple times, if that's not what you want, because Evas won't check if a callback existed before exactly as the one being registered (and thus, call it more than once on the event, in this case). This would make sense if you passed different functions and/or callback data, only.
-
Example:
- See the full example here.
| void* evas_object_event_callback_del | ( | Evas_Object * | obj, |
| Evas_Callback_Type | type, | ||
| Evas_Object_Event_Cb | func | ||
| ) |
Delete a callback function from an object.
- Since :
- 2.3
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj Object to remove a callback from [in] type The type of event that was triggering the callback [in] func The function that was to be called when the event was triggered
- Returns:
- The data pointer that was to be passed to the callback
- Remarks:
- This function removes the most recently added callback from the object
objwhich was triggered by the event typetypeand was calling the functionfuncwhen triggered. If the removal is successful it will also return the data pointer that was passed to evas_object_event_callback_add() when the callback was added to the object. If not successfulNULLwill be returned. -
Example:
extern Evas_Object *object; void *my_data; void up_callback(void *data, Evas *e, Evas_Object *obj, void *event_info); my_data = evas_object_event_callback_del(object, EVAS_CALLBACK_MOUSE_UP, up_callback);
| void* evas_object_event_callback_del_full | ( | Evas_Object * | obj, |
| Evas_Callback_Type | type, | ||
| Evas_Object_Event_Cb | func, | ||
| const void * | data | ||
| ) |
Delete (unregister) a callback function registered to a given Evas object event.
- Since :
- 2.3
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj Object to remove a callback from [in] type The type of event that was triggering the callback [in] func The function that was to be called when the event was triggered [in] data The data pointer that was to be passed to the callback
- Returns:
- The data pointer that was to be passed to the callback
- Remarks:
- This function removes the most recently added callback from the object
obj, which was triggered by the event typetypeand was calling the functionfuncwith datadata, when triggered. If the removal is successful it will also return the data pointer that was passed to evas_object_event_callback_add() (that will be the same as the parameter) when the callback was added to the object. In errors,NULLwill be returned. - For deletion of Evas object events callbacks filtering by just type and function pointer, use evas_object_event_callback_del().
-
Example:
extern Evas_Object *object; void *my_data; void up_callback(void *data, Evas *e, Evas_Object *obj, void *event_info); my_data = evas_object_event_callback_del_full(object, EVAS_CALLBACK_MOUSE_UP, up_callback, data);
| void evas_object_event_callback_priority_add | ( | Evas_Object * | obj, |
| Evas_Callback_Type | type, | ||
| Evas_Callback_Priority | priority, | ||
| Evas_Object_Event_Cb | func, | ||
| const void * | data | ||
| ) |
Add (register) a callback function to a given Evas object event with a non-default priority set. Except for the priority field, it's exactly the same as evas_object_event_callback_add.
- Since :
- 2.3
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj Object to attach a callback to [in] type The type of event that will trigger the callback [in] priority The priority of the callback, lower values called first. [in] func The function to be called when the event is triggered [in] data The data pointer to be passed to func
- See also:
- evas_object_event_callback_add
- Since (EFL) :
- 1.1
| Eina_Bool evas_object_freeze_events_get | ( | const Evas_Object * | obj | ) |
Determine whether an object is set to freeze (discard) events.
- Since :
- 2.3
- Returns:
- freeze whether
objis set to freeze events (EINA_TRUE) or not (EINA_FALSE)
- See also:
- evas_object_freeze_events_set()
- evas_object_pass_events_get()
- evas_object_repeat_events_get()
- evas_object_propagate_events_get()
- Since (EFL) :
- 1.1
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj The evas object
| void evas_object_freeze_events_set | ( | Evas_Object * | obj, |
| Eina_Bool | freeze | ||
| ) |
Set whether an Evas object is to freeze (discard) events.
- Since :
- 2.3
- Remarks:
- If
freezeisEINA_TRUE, it will make events onobjto be discarded. Unlike evas_object_pass_events_set(), events will not be passed to next lower object. This API can be used for blocking events whileobjis on transiting. -
If
freezeisEINA_FALSE, events will be processed on that object as normal.
- Warning:
- If you block only key/mouse up events with this API, we won't guarantee the state of the object, that only had key/mouse down events, will be.
- See also:
- evas_object_freeze_events_get()
- evas_object_pass_events_set()
- evas_object_repeat_events_set()
- evas_object_propagate_events_set()
- Since (EFL) :
- 1.1
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj The evas object [in] freeze pass whether objis to freeze events (EINA_TRUE) or not (EINA_FALSE)
| Eina_Bool evas_object_pass_events_get | ( | const Evas_Object * | obj | ) |
Determine whether an object is set to pass (ignore) events.
- Since :
- 2.3
- Returns:
- pass whether
objis set to pass events (EINA_TRUE) or not (EINA_FALSE)
- Remarks:
- Example:
- See the full example.
- See also:
- evas_object_pass_events_set()
- evas_object_repeat_events_get()
- evas_object_propagate_events_get()
- evas_object_freeze_events_get()
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj The evas object
| void evas_object_pass_events_set | ( | Evas_Object * | obj, |
| Eina_Bool | pass | ||
| ) |
Set whether an Evas object is to pass (ignore) events.
- Since :
- 2.3
- Remarks:
- If
passisEINA_TRUE, it will make events onobjto be ignored. They will be triggered on the next lower object (that is not set to pass events), instead (see evas_object_below_get()). -
If
passisEINA_FALSE, events will be processed on that object as normal.
- See also:
- evas_object_pass_events_get() for an example
- evas_object_repeat_events_set()
- evas_object_propagate_events_set()
- evas_object_freeze_events_set()
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj The evas object [in] pass whether objis to pass events (EINA_TRUE) or not (EINA_FALSE)
| Eina_Bool evas_object_propagate_events_get | ( | const Evas_Object * | obj | ) |
Retrieve whether an Evas object is set to propagate events.
- Since :
- 2.3
- Returns:
- whether
objis set to propagate events (EINA_TRUE) or not (EINA_FALSE)
- See also:
- evas_object_propagate_events_set()
- evas_object_repeat_events_get()
- evas_object_pass_events_get()
- evas_object_freeze_events_get()
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj The evas object
| void evas_object_propagate_events_set | ( | Evas_Object * | obj, |
| Eina_Bool | propagate | ||
| ) |
Set whether events on a smart object's member should get propagated up to its parent.
- Since :
- 2.3
- Remarks:
- This function has no effect if
objis not a member of a smart object. -
If
propisEINA_TRUE, events occurring on this object will be propagated on to the smart object of whichobjis a member. IfpropisEINA_FALSE, events occurring on this object will not be propagated on to the smart object of whichobjis a member. The default value isEINA_TRUE. All events are propagated from the child to parent between the smart members.
- See also:
- evas_object_propagate_events_get()
- evas_object_repeat_events_set()
- evas_object_pass_events_set()
- evas_object_freeze_events_set()
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj The evas object [in] propagate whether to propagate events ( EINA_TRUE) or not (EINA_FALSE)
| Eina_Bool evas_object_repeat_events_get | ( | const Evas_Object * | obj | ) |
Determine whether an object is set to repeat events.
- Since :
- 2.3
- Returns:
- whether
objis set to repeat events (EINA_TRUE) or not (EINA_FALSE)
- See also:
- evas_object_repeat_events_set() for an example
- evas_object_pass_events_get()
- evas_object_propagate_events_get()
- evas_object_freeze_events_get()
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj The evas object
| void evas_object_repeat_events_set | ( | Evas_Object * | obj, |
| Eina_Bool | repeat | ||
| ) |
Set whether an Evas object is to repeat events.
- Since :
- 2.3
- Remarks:
- If
repeatisEINA_TRUE, it will make events onobjto also be repeated for the next lower object in the objects' stack (see see evas_object_below_get()). -
If
repeatisEINA_FALSE, events occurring onobjwill be processed only on it. -
Example:
- See the full example.
- See also:
- evas_object_repeat_events_get()
- evas_object_pass_events_set()
- evas_object_propagate_events_set()
- evas_object_freeze_events_set()
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj The evas object [in] repeat whether objis to repeat events (EINA_TRUE) or not (EINA_FALSE)