USB Host
You can use the USB host functionality to learn about connected USB devices and communicate with them on the USB protocol layer.
This API is supported on specifc Tizen devices that support USB host features.
Figure: USB host mode overview
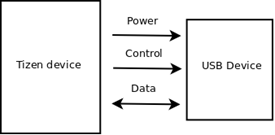
The main features of the USB Host API include:
-
Initializing the interface context
You can set up your application for the USB host functionality by initializing the interface context.
-
Finding and opening a device through a device list
To use the USB host functionality, you have to find a device and gather information about it. You can also monitor when a USB device is attached or detached.
-
Finding interface and endpoints
You can find the correct interface and configuration to connect to a device using USB.
-
Transferring data
You can claim an interface and send or receive data between 2 devices.
The following figure shows an overview of the USB host architecture.
Figure: USB host architecture
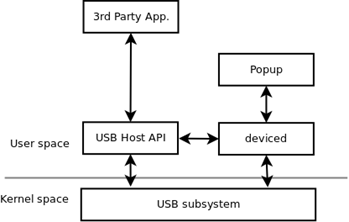
Prerequisites
To enable your application to use the USB host functionality:
- To use the USB host features, include the following feature in your tizen-manifest.xml file.
<feature name="http://tizen.org/feature/usb.host"/>
-
The USB Host API does not require any Tizen privileges to be defined, instead the user is asked for confirmation when performing a potentially privileged operation.
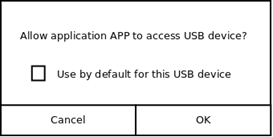
-
To use the methods and properties of the Tizen.System.Usb namespace, include it in your application:
C#Copyusing Tizen.System.Usb;
Finding and Opening a Device
To begin working with a device, you must find it in the device list.
-
Get the device list:
C#Copyvar usb = new UsbManager(); var devices = usb.AvailableDevices(); foreach (UsbDevice dev in devices) { ... -
Gather information about the device by inspecting
UsbDeviceproperties.Various USB Host API functions allow you to get some basic information about the USB devices in the device list. You can get values, such as vendor ID or product ID, from the descriptors sent by the device. By checking the device information, you can select a device suitable for your communication needs. Usually, the USB device vendor ID and product ID are used to uniquely identify the device.
All the USB Host API functions can operate on a device even if it has not been opened.
-
Open the device.
After the device is uniquely identified and you have found the one you need, open it for further use:
C#Copyforeach (UsbDevice dev in devices) { if (dev.UsbDeviceInformation.VendorId == 0x1234 && dev.UsbDeviceInformation.ProductId == 0x5678) { try { dev.Open(); -
While the device is open, you can get strings from it.
Identify the device using strings, such as the string associated with the manufacturer.
C#Copyvar str = dev.Strings; if (str.Manufacturer == "Samsung") { ... -
When the device is no longer needed, close it.
C#Copydev.Close(); dev.Dispose();
Monitoring Device Connections
To receive notifications when a USB device is attached or detached, use the DeviceHotPlugged event listener:
C#
Copy
var manager = new UsbManager();
manager.DeviceHotPlugged += ...;
Interfaces, Endpoints, and Transfer
USB communication always happens between the host and one of the endpoints. The endpoints are grouped into interfaces and interfaces into configurations. A device can have multiple configurations, but only one can be active at a time. All interfaces inside an active configuration can be used at the same time.
Programs which are dedicated for one specific device often hardcode the interface index and endpoints numbers. More flexible programs must go through a list of interfaces in a configuration, check the basic interface information (such as class), and check the endpoints. After finding a suitable interface, they claim it before starting communication with any of its endpoints.
C#
Copy
var device = manager.AvailableDevices.Single(...);
device.Configurations[123].SetAsActive();
var interface = device.ActiveConfiguration.Interfaces.Single(...); // or .Interfaces[123]
interface.Claim();
var endpoint = interface.Endpoints.Single(...); // or .Endpoints[123]
endpoint.Transfer(Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes("foobar"), 6, 1000); // timeout in ms
interface.Release();
Related information
- Dependencies
- Since Tizen 3.0
- API References