Voice Control Manager
Voice control manager features allow you to record voice and give responses for the recognized voice commands. You can register general and system voice commands such as “power on”, “power off”, “music play”, “music stop”, and so on. In addition, you can start and stop voice recording. When the voice recording is finished, you can receive multiple recognition results such as Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) and matched commands from the commands list, which is registered by the application using the voice control client.
The main features of the Tizen.Uix.VoiceControlManager namespace includes the following:
-
Creating a handle and registering event handlers.
- You can create a voice control manager handle and only one voice control manager instance can work on the device.
- You can get notifications of state changes, language changes, recognition results, and errors by registered event handlers.
-
Managing commands
- You can register commands as System, Widget, Foreground, SystemBackground, and Background type on the voice control service. When you speak a registered command, the callback returns the recognized result.
-
Starting, stopping, and canceling recognition.
- You can start and stop voice recording using a microphone.
- You can set it to stop recording manually or automatically. If the automatic stop is set, the voice control manager stops recording when the end of speech is detected.
- When the voice recording finishes, the voice control service recognizes the speech data and finds matching commands among the registered commands.
-
Getting the recognition result.
- The recognition result is invoked by the registered event handler.
- You can get a matched command list from the voice control engine.
- You can select command among matched commands.
-
Retrieving information
- You can retrieve information from the voice control manager.
- Voice control manager state
- The state is changed by method calls and applied as a precondition for each method call.
- Voice control service state
- The voice control service states are controlled by starting and stopping command recognition.
- Current language
- You can get the current language that the voice control engine uses as a base to recognize your utterance.
- Only the commands based on the current language can be recognized. Therefore, your utterance must be in the current language.
- The current language can be changed in application settings or by changing the language on the device display.
- Supported language
- You can retrieve a list of supported languages to check whether the language that you want is supported.
- Voice control manager state
- You can retrieve information from the voice control manager.
To use the voice control manager, follow these steps:
-
Create a handle and register event handlers.
The initialization allows the voice control to distinguish your application from any other application that also uses voice control. Only one voice control manager instance can work on the device. Therefore, if another application including voice control manager exists, your application cannot work properly on the same device.
The registered callbacks can be notified of the changes in service status, current language, recognition results, and errors.
-
Set commands.
You can create a command list, and add or remove individual commands in the list. While creating an individual command, set the command text and type for each command handle. When all the commands are created and added to the command list, set the command list to the voice control manager for recognition.
-
Prepare the voice control manager.
The preparation connects the voice control service. When the connection is complete, the service state changes to
Ready.When the application initializes and prepares the voice control manager, the voice control service is invoked and connected for the background work. The service and the application communicate as server and client.
-
Get the recognized command result and ASR.
The recognized command result and ASR are sent through a registered callback. You can receive the command matching result that the user uttered. Multiple recognition results can happen if the duplicated commands are registered or you request multiple commands. In this case, you can select or reject the results using the
VoiceControlManagerClient.SetRecognizedCommandsSelectionDelegate()callback. -
When no longer needed, unset the voice control manager.
You must disconnect the voice control service and deinitialize the voice control manager using the
Unprepare()andDeinitialize()methods of the Tizen.Uix.VoiceControlManager.VoiceControlManagerClient class.
The figure is the overall configuration for voice control framework:
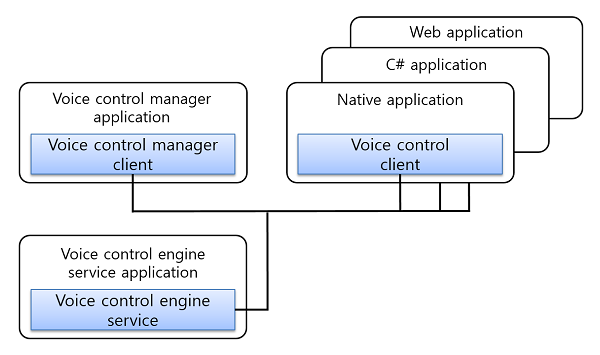
The voice control manager can cancel, start, or stop the voice control engine service voice recording. Additionally, the recognized result is received from the voice control engine service, then the voice control engine service analyzes voice recording data and delivers the perceived result to the manager. The voice control clients then register commands to recognize the voice recordings and register them in each application.
The following figure illustrates the voice control manager life-cycle:
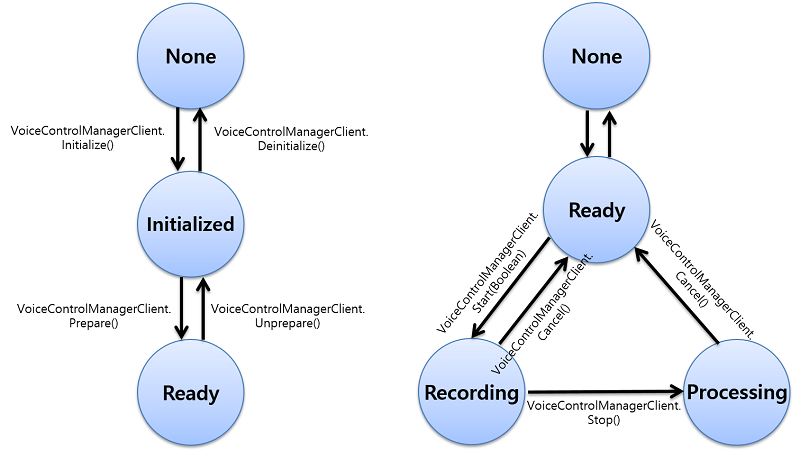
In general scenario, following are the voice control manager service state:
- The user starts recording for recognition by using a voice control manager application, button, or voice trigger. If the start is successful, the voice control service state changes to
Recording. For more information on service states, see Tizen.Uix.VoiceControlManager.ServiceState enumeration. - After the recording is completed, the service state changes to
Processingfor recognition processing. - After the recognition is completed, the service state changes to
Ready.
Prerequisites
To enable your application to use the voice control functionality, follow these steps:
-
To use the Tizen.Uix.VoiceControlManager class, the application has to request permission by adding the following privileges to the
tizen-manifest.xmlfile:C#Copy<privileges> <privilege>http://tizen.org/privilege/recorder</privilege> <privilege>http://tizen.org/privilege/voicecontrol.manager</privilege> </privileges> -
To use the methods and properties of the Tizen.Uix.VoiceControlManager class, include it in your application:
C#Copyusing Tizen.Uix.VoiceControlManager;Note
To use this privilege, your application must be signed with a platform-level certificate.
-
Initialize the voice control manager with the
Initialize()method of the Tizen.Uix.VoiceControlManager.VoiceControlManagerClient class:C#Copyvoid InitializeVoiceControlManager() { VoiceControlManagerClient.Initialize(); }If the method call is successful, the voice control state changes to
Initialized. The states are defined in the Tizen.Uix.VoiceControlManager.State enumeration.Note
The
Tizen.Uix.VoiceControlManagerclass is not thread safe. Do not use it in a thread. -
Prepare the voice control service with the
Prepare()method of the Tizen.Uix.VoiceControlManager.VoiceControlManagerClient class, which connects the background voice control service. The service records and recognizes the audio data and converts sound to text:C#Copyvoid PrepareVoiceControlManager() { VoiceControlManagerClient.Prepare(); }The
Prepare()method is asynchronous. When the preparation succeeds, the voice control state changes fromInitializedtoReady. The error callback is triggered if thePrepare()method fails. -
When the voice control manager is no longer needed, unprepare and deinitialize it:
C#Copyvoid UnpreparedVoiceControlManager() { VoiceControlManagerClient.Unprepare(); } void DeinitializeVoiceControlManager() { VoiceControlManagerClient.Deinitialize(); }When the
Unprepare()method of the Tizen.Uix.VoiceControlManager.VoiceControlManagerClient class succeeds, the voice control state changes fromReadytoInitialized.Note
Do not call the
Deinitialize()method of the Tizen.Uix.VoiceControlManager.VoiceControlManagerClient class in a callback. Within a callback, theDeinitialize()method fails and returnsErrorCode.OperationFailed.
Manage callbacks
You can set or unset callbacks such as notification of recognition results, state changes, errors, and so on:
NoteSet and unset all callbacks when the voice control manager state is
Initialized. For more information on theInitializedstates, see the Tizen.Uix.VoiceControlManager.State enumeration.
-
Set the state changed callback that is invoked when the voice control manager state changes:
C#Copy/// callback void stateChanged(object sender, StateChangedEventArgs e) { /// Your code } void SetUnsetStateChangedCb() { try { /// Set the callback VoiceControlManagerClient.StateChanged += stateChanged; /// Unset the callback VoiceControlManagerClient.StateChanged -= stateChanged; } catch (Exception e) { /// Error handling } } -
Set the service state changed callback to be invoked when the voice control manager service state changes:
C#Copy/// callback void serviceStateChanged(object sender, ServiceStateChangedEventArgs e) { /// Your code } void SetUnsetServiceStateChangedCb() { try { /// Set the callback VoiceControlManagerClient.ServiceStateChanged += serviceStateChanged; /// Unset the callback VoiceControlManagerClient.ServiceStateChanged -= serviceStateChanged; } catch (Exception e) { /// Error handling } } -
Set the current language changed callback invoked when the voice control setting language changes:
C#Copy/// callback void currentLanguageChanged(object sender, CurrentLanguageChangedEventArgs e) { /// Your code } void SetUnsetCurrentLanguageChangedCb() { try { /// Set the callback VoiceControlManagerClient.CurrentLanguageChanged += currentLanguageChanged; /// Unset the callback VoiceControlManagerClient.CurrentLanguageChanged -= currentLanguageChanged; } catch (Exception e) { /// Error handling } } -
Set the error callback to be invoked when an error occurs in the voice control manager process:
C#Copy/// callback void errorOccurred(object sender, ErrorOccurredEventArgs e) { /// Your code } void SetUnsetErrorOccurredCb() { try { /// Set the callback VoiceControlManagerClient.ErrorOccurred += errorOccurred; /// Unset the callback VoiceControlManagerClient.ErrorOccurred -= errorOccurred; } catch (Exception e) { /// Error handling } } -
Set the speech detected callback invoked when beginning of speech or end of speech is detected:
C#Copy/// callback void speechDetected(object sender, EventArgs e) { /// Your code } void SetUnsetSpeechDetectedCb() { try { /// Set the callback VoiceControlManagerClient.SpeechDetected += speechDetected; /// Unset the callback VoiceControlManagerClient.SpeechDetected -= speechDetected; } catch (Exception e) { /// Error handling } } -
Set the conversation requested callback that is invoked when the voice control manager or engine requests conversation for additional information about the current utterance:
C#Copy/// callback void conversationRequested(object sender, ConversationRequestedEventArgs e) { /// Your code } void SetUnsetConversationRequestedCb() { try { /// Set the callback VoiceControlManagerClient.ConversationRequested += conversationRequested; /// Unset the callback VoiceControlManagerClient.ConversationRequested -= conversationRequested; } catch (Exception e) { /// Error handling } } -
Set the private data updated callback invoked when the voice control engine sets private data to the voice control manager:
C#Copy/// callback void privateDataUpdated(object sender, PrivateDataUpdatedEventArgs e) { /// Your code } void SetUnsetPrivateDataUpdatedCb() { try { /// Set the callback VoiceControlManagerClient.PrivateDataUpdated += privateDataUpdated; /// Unset the callback VoiceControlManagerClient.PrivateDataUpdated -= privateDataUpdated; } catch (Exception e) { /// Error handling } } -
Set the specific engine result callback that is invoked when the voice control engine sends additional information about the undefined data:
C#Copy/// callback void specificEngineResult(object sender, SpecificEngineResultEventArgs e) { /// Your code } void SetUnsetSpecificEngineResultCb() { try { /// Set the callback VoiceControlManagerClient.SpecificEngineResult += specificEngineResult; /// Unset the callback VoiceControlManagerClient.SpecificEngineResult -= specificEngineResult; } catch (Exception e) { /// Error handling } } -
Set the pre recognition result updated callback invoked when voice control engine sets the pre recognition results (partial ASR) to voice control manager.
You can get the results of pre result event type and the pre recognition results, the partial ASR:
C#Copy/// callback void preRecognitionResultUpdated(object sender, PreRecognitionResultUpdatedEventArgs e) { /// Your code } void SetUnsetPreRecognitionResultUpdatedCb() { try { /// Set the callback VoiceControlManagerClient.PreRecognitionResultUpdated += preRecognitionResultUpdated; /// Unset the callback VoiceControlManagerClient.PreRecognitionResultUpdated -= preRecognitionResultUpdated; } catch (Exception e) { /// Error handling } } -
Set the all recognition result received callback invoked when the voice control engine sends all recognition results to the voice control manager.
In the callback, the recognized result, recognized text, and engine message results are included. Recognized results can include more than two voice commands if the two voice commands have the same command string and are registered by each voice control client.
If you want to select specific command in the recognized result, you can use
SetRecognizedCommandsSelectionDelegate()method:C#Copy/// callback void allRecognitionResultReceived(object sender, AllRecognitionResultEventArgs e) { /// Your code } void SetUnsetAllRecognitionResultReceivedCb() { try { /// Set the callback VoiceControlManagerClient.AllRecognitionResultReceived += allRecognitionResultReceived; /// Unset the callback VoiceControlManagerClient.AllRecognitionResultReceived -= allRecognitionResultReceived; } catch (Exception e) { /// Error handling } } -
Set the recognition result updated callback invoked when voice control engine updates the recognition result to voice control manager.
You can get the recognized result, recognized text, and recognized command list in this callback.
If no commands are matched, the callback returns
RecognizedResult.Rejected:C#Copy/// callback void recognitionResultUpdated(object sender, RecognitionResultUpdatedEventArgs e) { /// Your code } void SetUnsetRecognitionResultUpdatedCb() { try { /// Set the callback VoiceControlManagerClient.RecognitionResultUpdated += recognitionResultUpdated; /// Unset the callback VoiceControlManagerClient.RecognitionResultUpdated -= recognitionResultUpdated; } catch (Exception e) { /// Error handling } } -
Set the recognized commands selection callback invoked when the voice control manager select specific voice commands in all recognized result.
When an utterance is recognized, all the recognized results can include more than two voice commands if these commands have the same command string that is registered by each voice control client.
In this case, the voice control manager can select specific voice commands from all recognized results to send the voice control client using
SetRecognizedCommandsSelectionDelegate().You can select a valid command result from the recognized command selection:
C#Copy/// callback IEnumerable<VoiceCommand> recognizedCommandsSelection(IEnumerable<VoiceCommand> commands, string recognizedText, string message) { /// Your code return null; /// release commands. /// Select valid results } void SetUnsetRecognizedCommandsSelectionCb() { try { /// Set the callback VoiceControlManagerClient.SetRecognizedCommandsSelectionDelegate(recognizedCommandsSelection); /// Unset the callback VoiceControlManagerClient.SetRecognizedCommandsSelectionDelegate(null); } catch (Exception e) { /// Error handling } } -
Set a callback function to be called when engine sends audio formats necessary for playing TTS feedback:
C#Copy/// callback void feedbackAudioFormatChanged(object sender, FeedbackAudioFormatEventArgs e) { /// Your code } void SetUnsetFeedbackAudioFormatChangedCb() { try { /// Set the callback VoiceControlManagerClient.FeedbackAudioFormatChanged += feedbackAudioFormatChanged; /// Unset the callback VoiceControlManagerClient.FeedbackAudioFormatChanged -= feedbackAudioFormatChanged; } catch (Exception e) { /// Error handling } } -
Set a callback function to be called when engine sends audio streaming for TTS feedback:
C#Copy/// callback void feedbackStreaming(object sender, FeedbackStreamingEventArgs e) { /// Your code } void SetUnsetFeedbackStreamingCb() { try { /// Set the callback VoiceControlManagerClient.FeedbackStreaming += feedbackStreaming; /// Unset the callback VoiceControlManagerClient.FeedbackStreaming -= feedbackStreaming; } catch (Exception e) { /// Error handling } } -
Set TTS streaming callback function to be called when the voice control client (VC-Client) sends audio streaming for TTS feedback:
C#Copy/// callback void vcTtsStreaming(object sender, VcTtsStreamingEventArgs e) { /// Your code } void SetUnsetVcTtsStreamingCb() { try { /// Set the callback VoiceControlManagerClient.VcTtsStreaming += vcTtsStreaming; /// Unset the callback VoiceControlManagerClient.VcTtsStreaming -= vcTtsStreaming; } catch (Exception e) { /// Error handling } }
Start and stop recording
You can start, stop, or cancel recording using voice control manager by following these steps:
-
To start recording, use the
Start()method withexclusiveCommandOptionas the parameter. The connected voice control service starts recording and the voice control manager state is changed toRecording. If the parameterexclusiveCommandOptionvalue is true, the voice control service recognizes only the exclusive commands. This method must be called when the voice control manager is in theReadystate:C#Copyvoid StartManager(bool exclusiveCommandOption) { try { VoiceControlManagerClient.Start(exclusiveCommandOption); } catch (Exception e) { /// Error handling } } -
To stop recording, use the
Stop()method. The recording stops and the voice control manager state is changed toProcessing. When the recognition command result is processed, theRecognitionResultevent triggers and the state changes back toReady. This method must be called when the voice control manager is in theRecordingstate:C#Copyvoid StopManager() { try { VoiceControlManagerClient.Stop(); } catch (Exception e) { /// Error handling } } -
To cancel recording, use the
Cancel()method. This method must be called when the voice control manager is in theRecordingandProcessingstate:C#Copyvoid CancelManager() { try { VoiceControlManagerClient.Cancel(); } catch (Exception e) { /// Error handling } }
Send requests
Follow these steps to send requests using the voice control manager:
-
To send the event information to the voice control engine for purpose of activating specific action, use the
DoAction()method.This method must be called when the voice control manager is in the
Readystate:C#Copyvoid SendDoAction(SendEventType type, string sendEvent) { try { VoiceControlManagerClient.DoAction(type, sendEvent); } catch (Exception e) { /// Error handling } } -
To send the event and request message to a specific voice control engine, use the
SendSpecificEngineRequest()method.This method must be called when the voice control manager is in the
Readystate:C#Copyvoid SendSpecificEngineRequest(string engineAppId, string evt, string request) { try { VoiceControlManagerClient.SendSpecificEngineRequest(engineAppId, evt, request); } catch (Exception e) { /// Error handling } }
Retrieve voice control manager information
To get information about the current states, service states, current and supported languages, follow these steps:
-
Get the current voice control manager state using the
Stateproperty of the Tizen.Uix.VoiceControlManager.VoiceControlManagerClient class. The voice control manager state changes according to method calls:C#Copyvoid GetState() { State currentState; currentState = VoiceControlManagerClient.State; } -
Get the current voice control manager service state using the
ServiceStateproperty.If the application uses continuous recognition, the voice control service state can be changed from
Processingdirectly toRecording:C#Copyvoid GetServiceState() { ServiceState currentServiceState; currentServiceState = VoiceControlManagerClient.ServiceState; } -
Get the supported languages.
You can use the
GetSupportedLanguages()method of the Tizen.Uix.VoiceControlManager.VoiceControlManagerClient class. This function is used when the voice control manager is in theReadyorInitializedstate:C#Copyvoid GetSupportedLanguages() { try { List<string> list = (List<string>)VoiceControlManagerClient.GetSupportedLanguages(); } catch (Exception e) { /// Error handling } } -
Get the current language.
You can use the
CurrentLanguageproperty of the Tizen.Uix.VoiceControlManager.VoiceControlManagerClient class.Use the language change callback to get notifications for any language change.
This function is not used when the voice control manager is in the
Noneservice status:C#Copyvoid GetCurrentLanguage() { try { string currentLanguage = VoiceControlManagerClient.CurrentLanguage; } catch (Exception e) { /// Error handling } } -
Get the microphone volume during recording.
You can use the
RecordingVolumeproperty of the Tizen.Uix.VoiceControlManager.VoiceControlManagerClient class.The recording volume value is retrieved periodically with the short-term recorded sound data as decibels (dB).
The recording volume normally has a negative value, and 0 is the maximum value.
This function is used when the voice control manager is in the
Recordingservice state:C#Copyvoid GetRecordingVolume() { try { float recordingVolume = VoiceControlManagerClient.RecordingVolume; } catch (Exception e) { /// Error handling } } -
Get or set the audio in type.
You can use the
AudioTypeproperty of the Tizen.Uix.VoiceControlManager.VoiceControlManagerClient class.The audio type values can be
VC_AUDIO_ID_BLUETOOTHorVC_AUDIO_ID_MSFin string.This function is used when the voice control manager is in the
Readystate:C#Copyvoid GetSetAudioType() { try { /// Get string audioType = VoiceControlManagerClient.AudioType; /// Set VoiceControlManagerClient.AudioType = audioType; } catch (Exception e) { /// Error handling } } -
Get or set the recognition mode.
You can use the
RecognitionModeTypeenumeration of the Tizen.Uix.VoiceControlManager.RecognitionModeType enumeration as a parameter.The default value of
RecognitionModeTypeisRecognitionModeType.StopBySilence. If you want to set the manual mode, you can useRecognitionModeType.Manual.This function is used when the voice control manager is in the
Readystate:C#Copyvoid GetSetRecognitionMode() { try { /// Get RecognitionModeType recognitionModeType = VoiceControlManagerClient.RecognitionMode; /// Set VoiceControlManagerClient.RecognitionMode = recognitionModeType; } catch (Exception e) { /// Error handling } } -
Get or set private data between the voice control manager and the voice control engine.
You can use the
GetPrivateData()andSetPrivateData()methods of the Tizen.Uix.VoiceControlManager.VoiceControlManagerClient class.GetPrivateData()is used when the parameters move from the voice control engine to the voice control manager, whileSetPrivateData()is used when the parameters move from the voice control manager to the voice control engine.This option must be set when the voice control manager is in the
Readystate:C#Copyvoid GetSetPrivateData() { try { /// Get string privateData = VoiceControlManagerClient.GetPrivateData("privateKey"); /// Set VoiceControlManagerClient.SetPrivateData("privateKey", "privateData"); } catch (Exception e) { /// Error handling } }
Manage commands
You can use command group to manage the commands. You can add or remove the commands to the command group and retrieve the command information using the command group.
To create a command group and commands, follow these steps:
-
Create a command group with a command group handle.
The command group can have multiple commands. Each command has a text and a type.
The group can have
Background,Exclusive,Foreground,System,SystemBackground, andWidgettype commands.For more information on the command types, see Tizen.Uix.VoiceControlManager.CommandType enumeration.
Note
The order of command group priority is
System,Widget,Foreground,SystemBackground, andBackground. TheExclusiveis used on special situation. Normally, theSystemandSystemBackgroundcommands are only registered in the voice control manager. TheForegroundandBackgroundcommands are used in the voice control client application. Thewidgetcommand is automatically registered in the elementary on the screen. TheExclusivecommands have special priority, so these are used when recording starts withVoiceControlManagerClient.Start(true). When recording starts withVoiceControlManagerClient.Start(true), commands having other priorities are not recognized, onlyExclusivecommands are recognized.Create the command group:
C#Copyvoid CreateCommandGroup() { try { VoiceCommandsGroup group = new VoiceCommandsGroup(); } catch (Exception e) { /// Error handling } } -
Create a command.
First create a command handle, and then define the command and type:
C#Copyvoid CreateCommand() { try { VoiceCommand command = new VoiceCommand(); command.Command = "open"; command.Type = CommandType.Foreground; } catch (Exception e) { /// Error handling } } -
Add the command to the command group:
C#Copyvoid AddCommand() { try { VoiceCommandsGroup group = new VoiceCommandsGroup(); VoiceCommand command = new VoiceCommand(); command.Command = "open"; command.Type = CommandType.Foreground; group.Commands.Add(command); } catch (Exception e) { /// Error handling } }If necessary, you can also remove commands from the command group:
C#Copyvoid RemoveCommand() { try { VoiceCommand command = new VoiceCommand(); command.Command = "open"; command.Type = CommandType.Foreground; /// Other actions group.Commands.Remove(command); } catch (Exception e) { /// Error handling } }To retrieve the commands, you have to add the command list:
-
You can use the
GetCurrentCommands()method of the Tizen.Uix.VoiceControlManager.VoiceControlManagerClient class to get all commands from the command list:C#Copyvoid ForeachCommand() { try { IEnumerable<VoiceCommand> command = VoiceControlManagerClient.GetCurrentCommands(); } catch (Exception e) { /// Error handling } } -
You can use the
Commandsproperty of the Tizen.Uix.VoiceControlManager.VoiceCommandsGroup class to get the current commands in an output parameter.C#Copyvoid GetCommands() { try { VoiceCommand current_command = new VoiceCommand(); VoiceCommandsGroup group = new VoiceCommandsGroup(); /// Other actions current_commands = group.Commands; } catch (Exception e) { /// Error handling } }
-
-
Register the commands for recognition by setting the command group to the voice control service.
If you want to update the registered commands, set the command group again with the updated commands:
C#Copyvoid SetCommand() { try { VoiceCommandsGroup group = new VoiceCommandsGroup(); VoiceCommand command = new VoiceCommand(); command.Command = "test"; command.Type = CommandType.Foreground; group.Commands.Add(command); VoiceControlManagerClient.SetCommands(group); } catch (Exception e) { /// Error handling } } -
When no longer needed, unset the command group:
C#Copy/// Unset the command group void UnsetCommand() { try { VoiceCommandsGroup group = new VoiceCommandsGroup(); VoiceCommand command = new VoiceCommand(); command.Command = "test"; command.Type = CommandType.Foreground; group.Commands.Remove(command); VoiceControlManagerClient.SetCommands(group); ///or VoiceControlManagerClient.ClearCommands(); } catch (Exception e) { /// Error handling } }
Register command
-
You can register the commands for recognition by setting the command group to the voice control service from a file that includes the commands. The parameter
commandFilePathis used to get the path of the file. If you want to update the registered commands, set the command group again with the updated commands:C#Copyvoid SetCommandsFromFile(string commandFilePath) { try { /// file path contents. /* { "foreground": [ { "format": "0", "domain": "0", "cmd": "open" }, { "format": "0", "domain": "0", "cmd": "test" } ] } */ VoiceControlManagerClient.SetCommandsFromFile(commandFilePath, CommandType.Foreground); } catch (Exception e) { /// Error handling } } -
Checks whether the command format is supported:
C#Copyvoid GetSupportedCommandFormat() { try { bool isSupported = VoiceControlManagerClient.IsSupportedCommandFormat(CommandFormat.Action); } catch (Exception e) { /// Error handling } } -
Enable or disable command type as candidate command:
C#Copyvoid EnableDisableCommandType(CommandType cmdType) { try { VoiceControlManagerClient.EnableCommandType(cmdType); VoiceControlManagerClient.DisableCommandType(cmdType); } catch (Exception e) { /// Error handling } }
Related information
-
Dependencies
- Tizen 5.5 and Higher
-
API References
- Tizen.Uix.VoiceControlManager
- Tizen.Uix.VoiceControlManager.VoiceControlManagerClient
- Tizen.Uix.VoiceControlManager.ServiceState
- Tizen.Uix.VoiceControlManager.State
- Tizen.Uix.VoiceControlManager.RecognitionModeType
- Tizen.Uix.VoiceControlManager.CommandType
- Tizen.Uix.VoiceControlManager.VoiceCommandsGroup