Voice Control
Voice control features allow the user to control the device through their voice. You can register general voice commands, which allow you to recognize the sound data recorded by the user and send the result as a predefined command using the voice control service.
The main features of the Tizen.Uix.VoiceControl namespace includes:
-
Managing commands
You can use the voice control service to register commands as foreground or background type. When the user speaks a registered command, the callback returns the recognition result.
-
Retrieving information
You can get various information from the voice control:
-
Voice control state
The state is changed by method calls and applied as a precondition of each method call.
-
Voice control service state
The user controls the state by starting and stopping command recognition.
-
Current language
A command is valid only when the command language is the same as the current language. The current language can be changed by changing the application or display language on the device.
You can get a notification of the language change in a callback. If the display language is changed to a non-supported one, the voice control language changes to English.
-
Supported language
You can retrieve a list of supported languages to check whether the language that you want is supported.
-
To use the voice control, follow these steps:
-
Set up voice control and register callbacks.
The initialization allows the voice control to distinguish your application from any other applications also using voice control. The registered callbacks allow you to receive notifications about changes in the service state, language, and recognition result, and about any errors.
-
Prepare the voice control.
The preparation connects the voice control service for background work, such as recording and recognizing the user’s voice.
When the application initializes and prepares the voice control, the voice control daemon is invoked and connected for background work. The daemon and the application communicate as server and client.
-
Set commands.
You can create a command list, and add or remove individual commands in the list. When creating an individual command, set the command text and type for each command handle. When all commands are created and added to the command list, set the command list to the voice control for recognition.
-
Get the recognition result.
The recognition result is sent through a registered callback.
If the registered command is duplicated or the user speaks multiple commands, the recognition result can contain multiple results. If you set duplicated commands, the voice control service can reject the command. The rejection is shown in the result event.
-
When no longer needed, unprepare and deinitialize the voice control.
You must disconnect the voice control service and deinitialize the voice control using the
Unprepare()andDeinitialize()methods of the Tizen.Uix.VoiceControl.VoiceControlClient class.
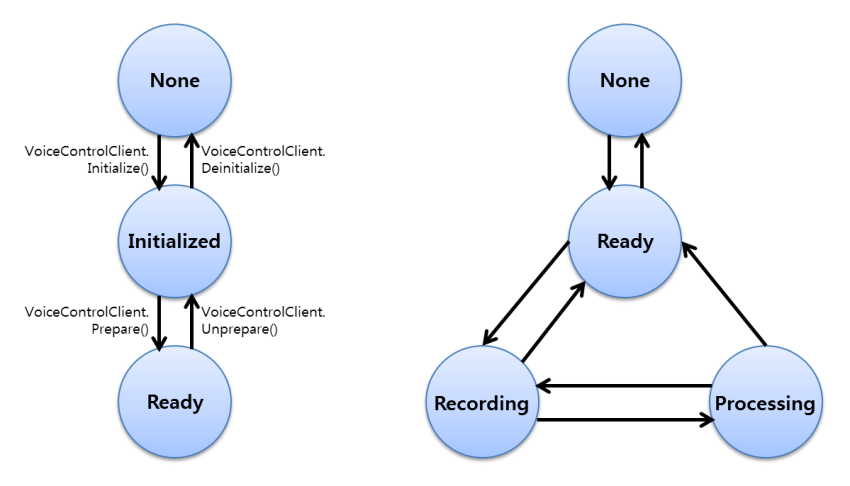
The following figure illustrates the voice control life-cycle states.
Figure: voice control (left) and voice control service (right) life-cycle states
Prerequisites
To enable your application to use the voice control functionality, follow these steps:
-
To use the methods and properties of the Tizen.Uix.VoiceControl.VoiceControlClient class, include it in your application:
C#Copyusing Tizen.Uix.VoiceControl.VoiceControlClient; -
Initialize the voice control with the
Initialize()method of theTizen.Uix.VoiceControl.VoiceControlClientclass:C#Copyvoid initialize_voice_control() { VoiceControlClient.Initialize(); }If the method call is successful, the voice control state changes to
Initialized(the states are defined in the Tizen.Uix.VoiceControl.State enumeration).Note
The voice control feature is not thread-safe and depends on the Ecore main loop. Implement voice control within the Ecore main loop and do not use it in a thread.
-
Prepare the voice control service with the
Prepare()method of theTizen.Uix.VoiceControl.VoiceControlClientclass, which connects the background voice control daemon. The daemon records and recognizes audio data and converts sound to text:C#Copyvoid prepare_vc() { VoiceControlClient.Prepare(); }The
Prepare()method is asynchronous, and when the preparation succeeds, the voice control state changes fromInitializedtoReady. If thePrepare()method fails, the error callback is triggered. -
When the voice control is no longer needed, unprepare and deinitialize it:
C#Copyvoid unprepared_vc() { VoiceControlClient.Unprepare(); } void deinitialize_voice_control() { VoiceControlClient.Deinitialize(); }When the
Unprepare()method of theTizen.Uix.VoiceControl.VoiceControlClientclass succeeds, the voice control state changes fromReadytoInitialized.Note
Do not call the
Deinitialize()method of theTizen.Uix.VoiceControl.VoiceControlClientclass in a callback. Within a callback, theDeinitialize()method fails and returnsErrorCode.OperationFailed.
Manage callbacks
To set and unset callbacks to get notifications about recognition results, state changes, and errors, follow these steps:
NoteSet and unset all callbacks when the voice control state is
Initialized(the states are defined in the Tizen.Uix.VoiceControl.State enumeration).
-
Set the state change callback to be invoked when the voice control state changes:
C#Copy/// Callback void VoiceControlStateChanged(object sender, StateChangedEventArgs e) { /// Your code } /// Set and unset void SetUnsetStateChangedCb() { try { VoiceControlClient.Initialize(); /// Set the callback for the StateChanged event VoiceControlClient.StateChanged += VoiceControlStateChanged; /// Unset the callback VoiceControlClient.StateChanged -= VoiceControlStateChanged; } catch (Exception e) { /// Error handling } } -
Set the service state change callback to be invoked when the voice control service state changes:
C#Copy/// Callback void VoiceControlServiceStateChanged(object sender, ServiceStateChangedEventArgs e) { /// Your code } /// Set and unset void SetUnsetServiceStateChangedCb() { try { VoiceControlClient.Initialize(); /// Set the callback for the ServiceStateChanged event VoiceControlClient.ServiceStateChanged += VoiceControlServiceStateChanged; /// Unset the callback VoiceControlClient.ServiceStateChanged -= VoiceControlServiceStateChanged; } catch (Exception e) { /// Error handling } } -
Set the current language change callback to be invoked when the system or application language changes:
C#Copy/// Callback void VoiceControlCurrentLanguageChanged(object sender, CurrentLanguageChangedEventArgs e) { /// Your code } /// Set and unset void SetUnsetCurrentLanguageChangedCb() { try { VoiceControlClient.Initialize(); /// Set the callback for the CurrentLanguageChanged event VoiceControlClient.CurrentLanguageChanged += VoiceControlCurrentLanguageChanged; /// Unset the callback VoiceControlClient.CurrentLanguageChanged -= VoiceControlCurrentLanguageChanged; } catch (Exception e) { /// Error handling } } -
Set the recognition result callback to be invoked when a voice command is recognized.
Note
If the recognition result produces a reject event, the voice control service has rejected the recognized command. Make sure that the command does not conflict with other commands and there are no duplicated commands.
To get the command, use the methods of the Tizen.Uix.VoiceControl.VoiceCommandList class, which represents a list of recognized commands. The
Commandproperty of the Tizen.Uix.VoiceControl.VoiceCommand class contains the recognized text:C#Copy/// Callback void VoiceControlRecognitionResult(object sender, RecognitionResultEventArgs e) { /// Your code } /// Set and unset void SetUnsetRecognitionResultCb() { try { VoiceControlClient.Initialize(); /// Set the callback for the RecognitionResult event VoiceControlClient.RecognitionResult += VoiceControlRecognitionResult; /// Unset the callback VoiceControlClient.RecognitionResult -= VoiceControlRecognitionResult; } catch (Exception e) { /// Error handling } } -
Set the error callback to be invoked when an error occurs in the voice control process:
C#Copy/// Callback void VoiceControlErrorOccured(object sender, ErrorOccuredEventArgs e) { /// Your code } /// Set and Unset void SetUnsetErrorOccuredCb() { try { VoiceControlClient.Initialize(); /// Set the callback for the ErrorOccured event VoiceControlClient.ErrorOccured += VoiceControlErrorOccured; /// Unset the callback VoiceControlClient.ErrorOccured -= VoiceControlErrorOccured; } catch (Exception e) { /// Error handling } }
Retrieve voice control information
To get information about the current states, and current and supported languages, follow these steps:
-
Get the current voice control state using the
Stateproperty of the Tizen.Uix.VoiceControl.VoiceControlClient class.The voice control state changes according to method calls when the voice control is, for example, initialized and prepared:
C#Copyvoid get_state() { State current_state; current_state = VoiceControlClient.State; } -
Get the current voice control service state using the
ServiceStateproperty.The user controls the voice control service state. In a general scenario:
- The user starts recording for recognition by using a voice application, button, or voice trigger. If the start is successful, the voice control service state changes to
Recording(the states are defined in the Tizen.Uix.VoiceControl.ServiceState enumeration). - After recording, the service state changes to
Processingfor recognition processing. - After recognition is completed, the service state returns to
Ready.
If the application uses continuous recognition, the voice control service state can be changed from
Processingdirectly toRecording:C#Copyvoid get_service_state() { ServiceState current_service_state; current_service_state = VoiceControlClient.ServiceState; } - The user starts recording for recognition by using a voice application, button, or voice trigger. If the start is successful, the voice control service state changes to
-
Get the supported languages with a foreach method that triggers a separate callback for each language.
As long as the callback returns
true, the foreach method continues to loop over the supported languages:C#Copyvoid get_supported_language() { try { VoiceControlClient.Initialize(); List<string> list = (List<string>)VoiceControlClient.GetSupportedLanguages(); } catch (Exception e) { /// Error handling } } -
Get the current language with the
CurrentLanguageproperty. The voice control recognition works for the current (default) language. Use the language change callback to be notified of language changes.
Manage commands
To create a command list and commands, follow these steps:
-
Create a command list with a command list handle.
The command list can include many commands, which each have a command text and type. The list can have both the
ForegroundandBackgroundtype commands (the types are defined in the Tizen.Uix.VoiceControl.CommandType enumeration. The foreground commands are valid when the application is in a visible state and the background commands are valid when the application is in a visible or invisible state.You can access the command list after you set it to the voice control and when you get the recognition result:
C#Copyvoid create_command_list() { try { VoiceCommandList list = new VoiceCommandList(); } catch (Exception e) { /// Error handling } } -
Create a command.
First create a command handle, and then define the command and type:
C#Copyvoid create_command() { try { VoiceCommand command = new VoiceCommand(); command.Command = "open"; command.Type = CommandType.Foreground; } catch (Exception e) { /// Error handling } } -
Add the command to the command list.
If necessary, you can also remove commands from the command list:
C#Copyvoid add_command() { try { VoiceCommandList list = new VoiceCommandList(); VoiceCommand command = new VoiceCommand(); command.Command = "open"; command.Type = CommandType.Foreground; list.Add(command); } catch (Exception e) { /// Error handling } } void remove_command() { try { VoiceCommand command = new VoiceCommand(); command.Command = "open"; command.Type = CommandType.Foreground; /// Other actions list.Remove(command); } catch (Exception e) { /// Error handling } }To retrieve the commands you have added to the command list:
-
You can use the
GetAllCommands()method of the Tizen.Uix.VoiceControl.VoiceCommandList class to get all commands from the command list:C#Copyvoid foreach_command() { try { VoiceCommandList VoiceControlCmdList = new VoiceCommandList(); List<VoiceCommand> list = (List<VoiceCommand>)VoiceControlCmdList.GetAllCommands(); } catch (Exception e) { /// Error handling } } -
You can use the
Currentproperty of theTizen.Uix.VoiceControl.VoiceCommandListclass to get the current command in an output parameter:Note
When you get the command handle with the
VoiceCommandList.Currentproperty, do not release it. To release the command handle, call theRemove()method of theVoiceCommandListclass before destroying theVoiceCommandobject.C#Copyvoid get_commands() { try { VoiceCommand current_command = new VoiceCommand(); VoiceCommandList cmd_list = new VoiceCommandList(); /// Other actions current_command = cmd_list.Current; } catch (Exception e) { /// Error handling } }
-
-
Register the commands for recognition by setting the command list to the voice control.
If you want to update registered commands, set the command list again with the updated commands:
C#Copyvoid set_command() { try { VoiceCommandList list = new VoiceCommandList(); VoiceCommand command = new VoiceCommand(); command.Command = "test"; command.Type = CommandType.Foreground; list.Add(command); VoiceControlClient.SetCommandList(list, CommandType.Foreground); } catch (Exception e) { /// Error handling } } -
When no longer needed, unset the command list:
C#Copy/// Unset the command list void unset_command() { try { VoiceCommandList list = new VoiceCommandList(); VoiceCommand command = new VoiceCommand(); command.Command = "test"; command.Type = CommandType.Foreground; list.Add(command); VoiceControlClient.UnsetCommandList(CommandType.Foreground); } catch (Exception e) { /// Error handling } }
Related information
-
Dependencies
- Tizen 4.0 and Higher
-
API References