Media Recording
Tizen offers basic recorder features, including an audio and video recorder.
The main features of the Recorder API include:
-
Recording audio
You can record audio after you have prepared the audio recorder.
-
Recording video
You can record a video after you have prepared the video recorder.
The following file formats are supported:
- Video:
mp4and3gp - Audio:
m4aandamr
Valid input sources consist of internal and external microphones and a camera. The used input audio or video source depends on the currently connected audio path and camera module of the device. The recorder APIs in the video recorder serve as the interface with the hardware. Input is processed through that handle.
During testing, you can use the emulator to imitate audio or video recording, as long as your computer has a proper input source device.
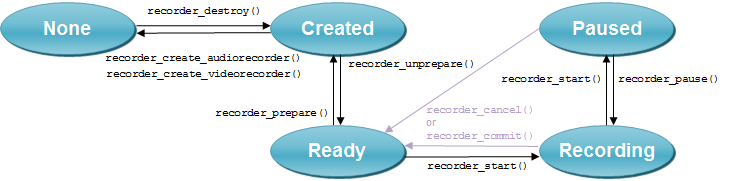
The following figure illustrates the general recorder state changes.
Figure: Recorder states
Note
While running applications on the emulator, audio-video synchronization errors can occur due to the computer performance.
Prerequisites
To use the functions and data types of the Recorder and Camera APIs, include the <camera.h> and <recorder.h> header files in your application:
#include <recorder.h>
#include <camera.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
In this guide, you also need the <stdio.h> and <unistd.h> header files to use standard file input and output functions and system calls.
Preparing the Audio Recorder
To initialize the audio recorder for use:
-
To create a handle for the audio recorder, use the
recorder_create_audiorecorder()function:static recorder_h g_recorder; /* Create the audio recorder handle */ int error_code = recorder_create_audiorecorder(&g_recorder); if (error_code == RECORDER_ERROR_NONE) dlog_print(DLOG_INFO, LOG_TAG, "error code = %d", error_code); else dlog_print(DLOG_ERROR, LOG_TAG, "error code = %d", error_code);The function sets the audio recorder state to
RECORDER_STATE_CREATED. -
To receive a notification whenever the audio recorder state changes:
-
Register a callback using the
recorder_set_state_changed_cb()function:error_code = recorder_set_state_changed_cb(g_recorder, _state_changed_cb, NULL); -
Define the state change callback.
The following example code implements a simple callback that prints the previous and current audio recorder states:
static void _state_changed_cb(recorder_state_e previous, recorder_state_e current, bool by_policy, void *user_data) { dlog_print(DLOG_INFO, LOG_TAG, "_recorder_state_changed_cb (prev: %d, curr: %d)\n", previous, current); }
-
3. To set various audio recording attributes:
-
Set the audio codec for encoding the audio stream using the
recorder_set_audio_encoder()function:#define FILENAME_PREFIX "AUDIO" struct tm localtime = {0}; time_t rawtime = time(NULL); char filename[256] = {'\0'}; size_t size; /* Set the audio encoder */ error_code = recorder_set_audio_encoder(g_recorder, RECORDER_AUDIO_CODEC_AAC); /* Set the audio sample rate */ error_code = recorder_attr_set_audio_samplerate(rec_data.recorder, 44100);The possible audio codec values are defined in the
recorder_audio_codec_eenumeration.Note
In the emulator, set the sample rate to 44100 and use a stereo channel with the AAC codec, and set the sample rate below 8000 and use a mono channel with the AMR codec. -
Based on the audio codec, set the correct file format using the
recorder_set_file_format()function. For example, if you set the codec to AAC, set the file format to 3GP./* Set the file format according to the audio encoder */ error_code = recorder_set_file_format(g_recorder, RECORDER_FILE_FORMAT_3GP);The possible file format values are defined in the
recorder_file_format_eenumeration. -
Based on the file format, define the correct file name, and set it using the
recorder_set_filename()function. The function takes as a parameter the full path and name of the file to which the recorded audio data is to be stored./* Create the file name */ if (localtime_r(&rawtime, &localtime) != NULL) { size = snprintf(filename, sizeof(filename), "%s/%s-%04i-%02i-%02i_%02i:%02i:%02i.3gp", app_get_data_path(), FILENAME_PREFIX, localtime.tm_year + 1900, localtime.tm_mon + 1, localtime.tm_mday, localtime.tm_hour, localtime.tm_min, localtime.tm_sec); } else { /* Error handling */ } /* Set the full path and file name */ /* Set the file name according to the file format */ error_code = recorder_set_filename(g_recorder, filename); -
Set the file size limit, encoder bitrate, audio device, and sample rate:
/* Set the maximum file size to 1024 (kB) */ error_code = recorder_attr_set_size_limit(g_recorder, 1024); /* Set the audio encoder bitrate */ error_code = recorder_attr_set_audio_encoder_bitrate(g_recorder, 28800); /* Set the audio device to microphone */ error_code = recorder_attr_set_audio_device(g_recorder, RECORDER_AUDIO_DEVICE_MIC); /* Set the audio sample rate */ error_code = recorder_attr_set_audio_samplerate(g_recorder, 44100);The possible audio device values are defined in the
recorder_audio_device_eenumeration.
For more information on available attributes, see the Attributes API.
-
To receive a notification when the audio recorder reaches the recording limit:
-
Register a callback using the
recorder_set_recording_limit_reached_cb()function:error_code = recorder_set_recording_limit_reached_cb(g_recorder, _recorder_recording_limit_reached_cb, NULL); -
Define the recording limit callback.
The following example code implements a simple callback that prints a notification about reaching the recording limit:
static void _recorder_recording_limit_reached_cb(recorder_recording_limit_type_e type, void *user_data) { dlog_print(DLOG_DEBUG, LOG_TAG, "Recording limit reached: %d\n", type); }
-
Recording Audio
To record audio:
-
Prepare the audio recorder using the
recorder_prepare()function:error_code = recorder_prepare(g_recorder);The function sets the audio recorder state to
RECORDER_STATE_READY. -
Start recording audio using the
recorder_start()function. If the target file path and name have been set to an existing file, the existing file is replaced with a new file.error_code = recorder_start(g_recorder);The function sets the audio recorder state to
RECORDER_STATE_RECORDING. -
To pause and resume recording:
-
Check the audio recorder state using the
recorder_get_state()function:error_code = recorder_get_state(g_recorder, &state);If the state is
RECORDER_STATE_RECORDING, you can pause recording. -
Pause recording using the
recorder_pause()function:error_code = recorder_pause(g_recorder);The function sets the audio recorder state to
RECORDER_STATE_PAUSED. -
Resume recording using the
recorder_start()function.
-
-
To stop recording:
-
Check the audio recorder state using the
recorder_get_state()function. If the state isRECORDER_STATE_RECORDINGorRECORDER_STATE_PAUSED, you can stop recording. -
To stop recording:
- To discard the recording, use the
recorder_cancel()function. - To save the recorded data, use the
recorder_commit()function.
Both functions set the audio recorder state to
RECORDER_STATE_READY.The following example code first checks the audio recorder state, and then stops the recorder and saves the recorded data to a file:
/* Check the audio recorder state */ static bool _recorder_expect_state(recorder_h recorder, recorder_state_e expected_state) { recorder_state_e state; int error_code = recorder_get_state(recorder, &state); dlog_print(DLOG_INFO, LOG_TAG, "recorder state = %d, expected recorder state = %d", state, expected_state); if (state == expected_state) return TRUE; return FALSE; } /* Stop the recorder and save the recorded data to a file */ if (_recorder_expect_state(g_recorder, RECORDER_STATE_RECORDING) || _recorder_expect_state(g_recorder, RECORDER_STATE_PAUSED)) { error_code = recorder_commit(g_recorder); if (error_code != RECORDER_ERROR_NONE) { dlog_print(DLOG_ERROR, LOG_TAG, "error code = %d", error_code); return true; } } - To discard the recording, use the
-
-
After you have finished recording, release all resources allocated to the audio recorder:
-
Deregister the recording limit callback using the
recorder_unset_recording_limit_reached_cb()function:error_code = recorder_unset_recording_limit_reached_cb(g_recorder); -
Reset the audio recorder using the
recorder_unprepare()function.error_code = recorder_unprepare(g_recorder);The function changes the audio recorder state from
RECORDER_STATE_READYtoRECORDER_STATE_CREATED. -
Deregister the state change callback using the
recorder_unset_state_changed_cb()function:error_code = recorder_unset_state_changed_cb(g_recorder); -
Release the audio recorder resources using the
recorder_destroy()function:error_code = recorder_destroy(g_recorder);The function sets the audio recorder state to
RECORDER_STATE_NONE.
-
Preparing the Video Recorder
To initialize the video recorder for use:
-
Define a structure for storing the camera and video recorder handles and a Boolean variable specifying whether the video recorder is switched off:
struct recdata { bool shutdown; recorder_h recorder; camera_h camera; }; -
Define variables for configuring the camera and video recorder:
static const int RECORD_TIME=2; static const int RECORD_LIMIT=4; #define FILENAME_PREFIX "VIDEO" static int g_bitrate = 288000; static int duration; static int playing=0; static int ret;
Configuring the Camera
To configure the camera:
-
Create the structure for the camera and video recorder handles:
static recdata rec_data;You can also declare variables to store, for example, the record time, video file paths, bit rate, record limit, flag, and return value.
-
Create the camera handle using the
camera_create()function. The function takes as parameters the camera handle and the hardware camera to access.int error_code = 0; rec_data.shutdown = FALSE; rec_data.camera = NULL; rec_data.recorder = NULL; /* Create the camera handle */ error_code = camera_create(CAMERA_DEVICE_CAMERA0, &rec_data.camera); if (error_code == CAMERA_ERROR_NONE) dlog_print(DLOG_INFO, LOG_TAG, "error code = %d", error_code); else dlog_print(DLOG_ERROR, LOG_TAG, "error code = %d", error_code);The function sets the camera state to
CAMERA_STATE_CREATED. To query the state, use thecamera_get_state()function. -
Set the display for the camera preview using the
camera_set_display()function. For more information, see Configuring the Camera and its Callbacks in the Camera guide.
Registering the Recording Limit Callback
To receive notifications about reaching the recording limit:
-
Register a callback using the
recorder_set_recording_limit_reached_cb()function:ret = recorder_set_recording_limit_reached_cb(rec_data.recorder, _recorder_recording_limit_reached_cb, 0); -
Define the recording limit callback.
The following example code implements a simple callback that prints a notification about reaching the recording limit:
static void _recorder_recording_limit_reached_cb(recorder_recording_limit_type_e type, void *user_data) { dlog_print(DLOG_DEBUG, "Video Recorder", "Recording limit reached: %d\n", type); } -
To test whether the callback works properly, use the
sleep()function to reach the recording limit:ret = recorder_start(rec_data.recorder); sleep(RECORD_LIMIT + 1); /* Waits longer than the recording limit */ ret = recorder_pause(rec_data.recorder);
Configuring the Video Recorder
To configure the video recorder:
-
To create the video recorder handle, use the
recorder_create_videorecorder()function. The function takes as parameters the camera handle and the video recorder handle./* Create the video recorder handle */ error_code = recorder_create_videorecorder(rec_data.camera, &rec_data.recorder); if (error_code == RECORDER_ERROR_NONE) dlog_print(DLOG_INFO, LOG_TAG, "error code = %d", error_code); else dlog_print(DLOG_ERROR, LOG_TAG, "error code = %d", error_code);The function sets the video recorder state to
RECORDER_STATE_CREATED. To query the state, use therecorder_get_state()function. -
To receive a notification whenever the video recorder state changes:
-
Register a callback using the
recorder_set_state_changed_cb()function:/* Set the state change callback for the video recorder */ error_code = recorder_set_state_changed_cb(rec_data.recorder, on_state_changed_cb, NULL); if (error_code == RECORDER_ERROR_NONE) dlog_print(DLOG_INFO, LOG_TAG, "error code = %d", error_code); else dlog_print(DLOG_ERROR, LOG_TAG, "error code = %d", error_code); -
Define the state change callback.
The following example code implements a simple callback that prints the previous and current video recorder states:
/* State change callback for the video recorder */ static void on_state_changed_cb(recorder_state_e previous, recorder_state_e current, bool by_asm, void *data) { dlog_print(DLOG_DEBUG, LOG_TAG, "_recorder_state_changed_cb (prev: %d, curr: %d)\n", previous, current); }
-
-
To set various video recording attributes:
-
To set the video codec for encoding the video stream:
-
Check which video codecs the device supports.
To check the codecs, use the
recorder_foreach_supported_video_encoder()function. The function takes as its second parameter a callback that is invoked once for each codec supported by the video recorder (defined in the first parameter).While the callback returns
true, the loop continues to the next supported codec, if any. The loop ends when the callback returnsfalse.In the following example code, the callback loop ends after finding the first supported codec:
recorder_video_codec_e supported_codec; static bool _video_encoder_cb(recorder_video_codec_e codec, void *user_data) { recorder_video_codec_e * supported_codec = (recorder_video_codec_e*)user_data; *supported_codec = codec; return false; } error_code = recorder_foreach_supported_video_encoder(rec_data.recorder, _video_encoder_cb, &supported_codec);The possible video codec values are defined in the
recorder_video_codec_eenumeration. -
Set the video codec using the
recorder_set_video_encoder()function:/* Set the video encoder for the video recorder */ error_code = recorder_set_video_encoder(rec_data.recorder, supported_codec);
-
-
To set the video encoder bitrate, use the
recorder_attr_set_video_encoder_bitrate()function:/* Set the video encoder bitrate */ error_code = recorder_attr_set_video_encoder_bitrate(rec_data.recorder, g_bitrate); -
To set the file format for the video file:
-
Check which file formats the device supports.
To check the formats, use the
recorder_foreach_supported_file_format()function. The function takes as its second parameter a callback that is invoked once for each format supported by the video recorder (defined in the first parameter). -
Set the file format using the
recorder_set_file_format()function. Make sure the file format matches the video codec./* Set the file format */ error_code = recorder_set_file_format(rec_data.recorder, RECORDER_FILE_FORMAT_MP4);The possible file format values are defined in the
recorder_file_format_eenumeration.
-
-
To set the file name, use the
recorder_set_filename()function. The function takes as a parameter the full path and name of the file to which the recorded video data is to be stored. Make sure the file extension matches the file format.struct tm localtime = {0}; time_t rawtime = time(NULL); char filename[256] = {'\0'}; size_t size; /* Create the file name */ if (localtime_r(&rawtime, &localtime) != NULL) { size = snprintf(filename, sizeof(filename), "%s/%s-%04i-%02i-%02i_%02i:%02i:%02i.mp4", app_get_data_path(), FILENAME_PREFIX, localtime.tm_year + 1900, localtime.tm_mon + 1, localtime.tm_mday, localtime.tm_hour, localtime.tm_min, localtime.tm_sec); } else { /* Error handling */ } /* Set the full path and file name */ error_code = recorder_set_filename(rec_data.recorder, filename); -
To set the audio encoder, audio encoder bitrate, and audio sample rate, use the
recorder_set_audio_encoder(),recorder_attr_set_audio_encoder_bitrate(), andrecorder_attr_set_audio_samplerate()functions, as with the audio encoder.
For more information on available attributes, see the Attributes API.
-
Recording a Video
To record a video:
-
Prepare the video recorder using the
recorder_prepare()function:/* Prepare the recorder */ error_code = recorder_prepare(rec_data.recorder);The function changes the video recorder state from
RECORDER_STATE_CREATEDtoRECORDER_STATE_READY. -
Start recording using the
recorder_start()function. If the target file path and name have been set to an existing file, the existing file is replaced with a new file./* Start the recorder */ error_code = recorder_start(rec_data.recorder);The function changes the video recorder state from
RECORDER_STATE_READYtoRECORDER_STATE_RECORDING. -
To pause and resume recording:
-
Pause recording using the
recorder_pause()function:/* Pause the recorder */ error_code = recorder_pause(rec_data.recorder);The function changes the video recorder state from
RECORDER_STATE_RECORDINGtoRECORDER_STATE_PAUSED. -
Resume recording using the
recorder_start()function.
-
-
To stop recording:
-
To stop recording without saving the recorded data, use the
recorder_cancel()function. No data is saved to the target file./* Stop the recorder without saving the recorded data */ error_code = recorder_cancel(rec_data.recorder); -
To stop recording and save the recorded data, use the
recorder_commit()function. The data is saved to the target file./* Stop the recorder and save the recorded data to a file */ error_code = recorder_commit(rec_data.recorder);
Both functions change the video recorder state from
RECORDER_STATE_RECORDINGorRECORDER_STATE_PAUSEDtoRECORDER_STATE_READY. -
-
After you have finished recording, release all resources allocated to the video recorder:
-
Deregister the recording limit callback using the
recorder_unset_recording_limit_reached_cb()function:/* Deregister the recording limit callback */ ret = recorder_unset_recording_limit_reached_cb(rec_data.recorder); -
Reset the video recorder using the
recorder_unprepare()function:/* Unprepare the recorder */ error_code = recorder_unprepare(rec_data->recorder);The function changes the video recorder state from
RECORDER_STATE_READYtoRECORDER_STATE_CREATED. -
Deregister the state change callback using the
recorder_unset_state_changed_cb()function:/* Deregister the state change callback */ error_code = recorder_unset_state_changed_cb(rec_data.recorder); -
Release the video recorder resources using the
recorder_destroy()function:/* Destroy the recorder handle */ error_code = recorder_destroy(rec_data.recorder);The function changes the video recorder state from
RECORDER_STATE_CREATEDtoRECORDER_STATE_NONE.
-
Related Information
- Dependencies
- Since Tizen 2.4