Application Signing and Certificates
Application signing is the process of digitally signing executables, scripts, and content of an application to confirm the application author and guarantee that the application has not been altered or corrupted since it was signed. The process employs the use of a cryptographic hash to validate authenticity and integrity.
Tizen requires that all applications are digitally signed with a proper signing key and certificate before they can be installed.
Through application signing, Tizen achieves the following goals:
- Ensuring application integrity: Users can download an application that has not been tampered with after development.
- Identifying the application developer: The applications with the same signing key are regarded as developed by the same developer. A set of applications with same developer’s signing key can share secured resources as the developer intended.
- Proof of store validation: An application store performs some validation checks before distributing an application. As the proof of store validation, the application store signs the application.
- Enforcing proper usage of privileged APIs: An application distributor, such as an application store, can restrict the API set used by the application by signing a key with a proper privilege.
Signature Type
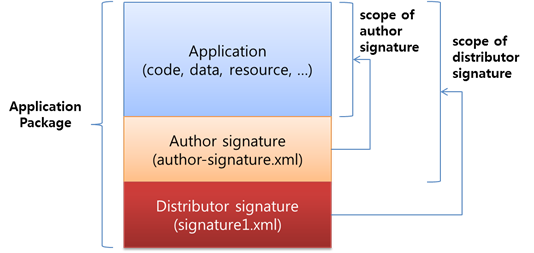
All Tizen applications must have at least 2 signatures:
- Author signature:
- You sign the author signature with your own author signing key in Tizen Studio.
- Applications with the same author signing key are regarded as developed by the same developer.
- Application update is allowed only when the author signature of the old version and the new version are signed with a same author signing key.
- A set of applications with a same author’s signing key can share secured resources as the author (developer) intended.
- Distributor signature:
- The distributor signature is signed by a distributor, such as the official site for Tizen applications, as the proof of application validation.
- The distributor signature determines the API set that the application can use.
Figure: Signature type
Certificate and API Privileges
Tizen API privileges represent the ability to use a certain set of sensitive APIs and secure system resources. The privileges are categorized into 3 levels according to their security and privacy level:
- Public level: used by any application developers.
- Partner level: used by developers with a business relationship with a device vendor.
- Platform level: exclusively used by a device vendor.
For an application to use a privileged API, the distributor signature must be generated from a certificate (and its signing key) with a proper privilege level. If an application has a distributor signature generated from a partner level certificate (and its signing key), the application can use only public and partner level APIs.
The following table shows the relationship between the certificate (and signing key) privilege level and the API privilege level.
Table: API levels allowed in specific certificate privilege levels
| Certificate privilege level | Public level API | Partner level API | Platform level API |
|---|---|---|---|
| Public level | Allowed | Not allowed | Not allowed |
| Partner level | Allowed | Allowed | Not allowed |
| Platform level | Allowed | Allowed | Allowed |
Signing Flow and Getting Certificates
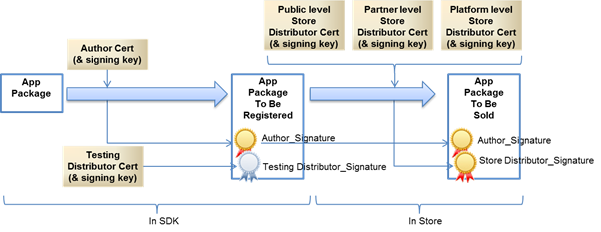
You can sign your application with your own author signing key and a testing distributor signing key in Tizen Studio. With those, you can install and test the application on your test device and an emulator.
When the application is submitted to a store after development, the store removes the testing distributor signature and adds the store distributor signature for the application release. Normal applications are signed with the public level distributor signing key in the store. Some applications granted from a device vendor are allowed to be signed with the partner level distributor signing key. Signing with the platform level distributor key is permitted only for the internal application of a device vendor or Tizen.
The following figure illustrates the signature and certificate flow.
Figure: Signature flow
The testing distributor certificate and its signing key with the public level are preloaded in Tizen Studio. The author certificate and its signing key can also be created in Tizen Studio. For more information, see Working with the Certificate Profile.
A device vendor can disallow unauthorized applications to be installed on its devices to protect its devices from viruses and malwares. Samsung also disallows unauthorized applications to be installed on its Tizen devices. In such cases, you must get an author certificate and a distributor certificate from the device vendor. For more information, see Issuing a Tizen Certificate and Running Applications in Commercial Devices.
Signature Specification
The application signing scheme of Tizen follows the specification of the XML Digital Signatures for Widgets specified by W3C.
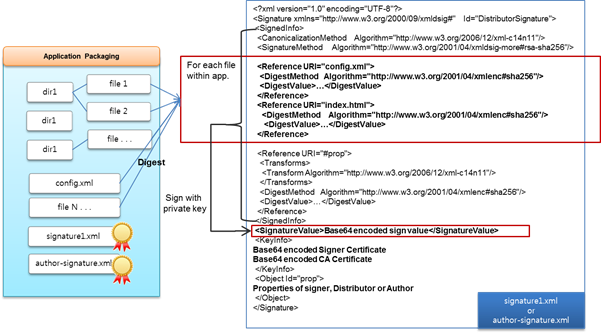
The following figure shows the signature file structure.
Figure: Signature file structure