Diagnostics
Diagnostics API is used to collect data from applications and services. This API also allows you to read crash reports if a process in the system crashes.
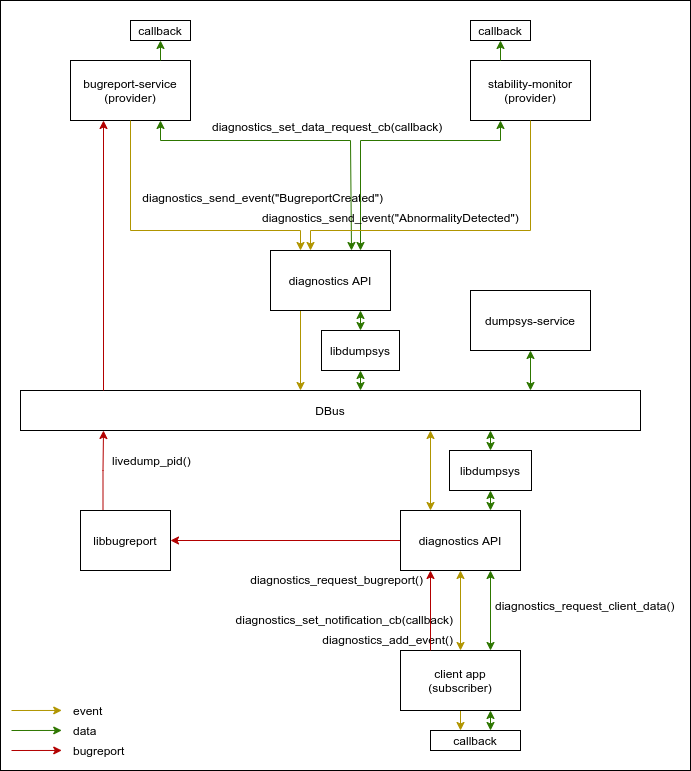
Figure: Diagnostics overall architecture
Prerequisites
To enable your application to use Diagnostics API:
-
To use Diagnostics API to collect diagnostics data, the application must be signed with a platform level distributor certificate.
To sign application with a platform level certificate:
-
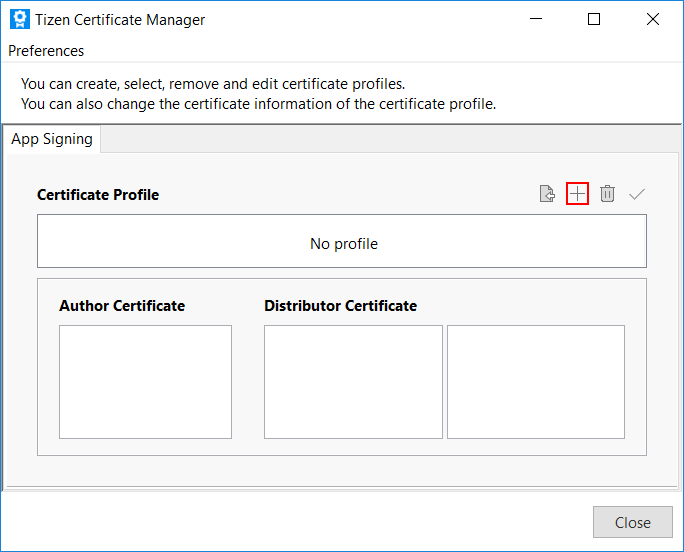
In Tizen Studio, select Tools > Certificate Manager.
-
To add a new certificate profile, click + in the Certificate Manager window.
-
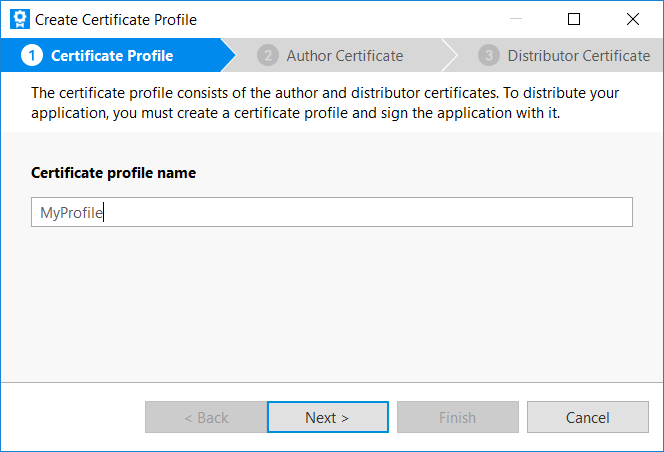
Enter the profile name and click Next.
-
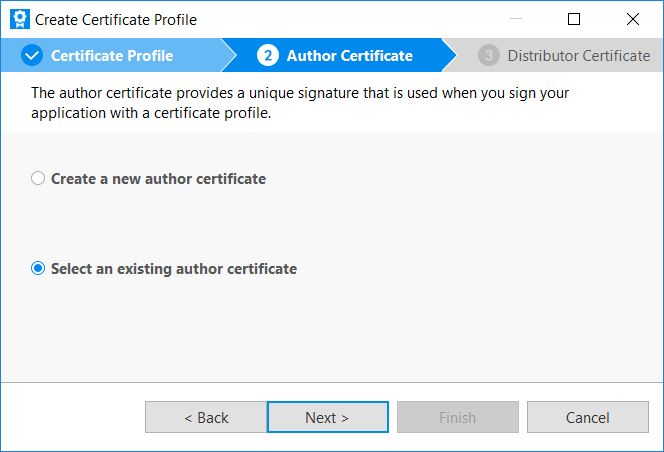
Select Select an existing author certificate and click Next.
-
Select an author certificate from the disk using Browse. Enter the password if needed and click Next.
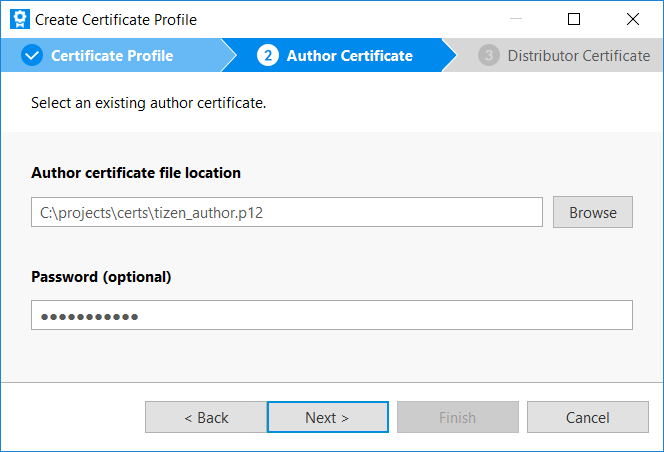
-
Select Select a distributor certificate for an another app store and click Next.
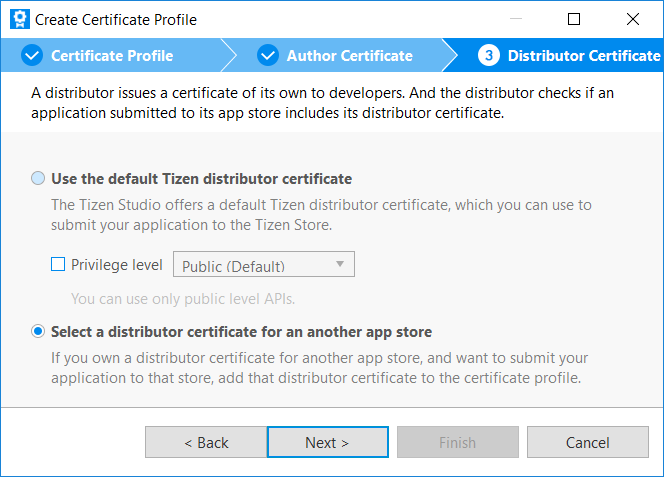
-
Click Browse and select the distributor certificate. Enter the password and click Finish.
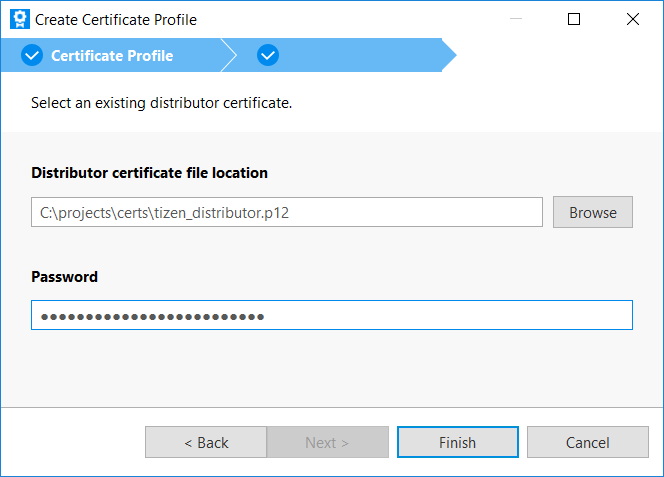
This newly added profile appears in the profile list.
-
Click Close.
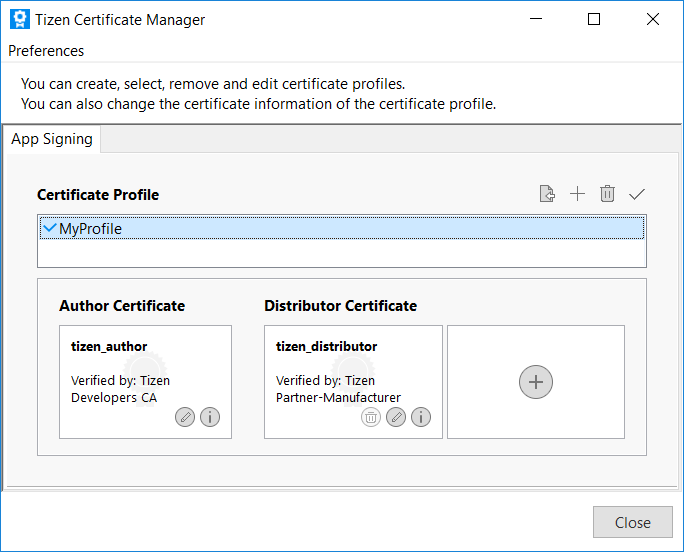
-
-
To use functions and data types of Diagnostics API, include the
<diagnostics.h>header file in your application:#include <diagnostics.h>
Diagnostic events
Diagnostics API allows you to send and receive diagnostic events. The events can contain additional data packed into the bundle.
To send diagnostic event, use diagnostics_send_event():
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
bundle *event_data = bundle_create();
// This is required for system services only, not applications
diagnostics_set_client_id("diagnostics-client");
bundle_add_str(event_data, "somekey", "somevalue");
diagnostics_send_event("ConnectionBroken", event_data);
bundle_free(event_data);
}
To receive diagnostic event, use diagnostics_subscribe_event() proceeded by diagnostics_set_notification_cb():
void notification_handler(diagnostics_ctx_h ctx, void *user_data)
{
...
diagnostics_destroy(ctx);
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
diagnostics_set_notification_cb(notification_handler, NULL);
diagnostics_subscribe_event("ConnectionBroken", "org.tizen.someapp");
}
Diagnostic data request
Diagnostics API also can request data from other applications or services, especially you can request the diagnostic data that could not be saved in the logs due to various reasons. For example, if the volume of data is too large, the data format is not supported as it is in binary or custom format, reports that are time-consuming to create, and so on, such data can now be requested using this API.
To do so, call diagnostics_request_client_data(). The client_id variable must be the id of the process that supports Diagnostics API requests:
void request_data()
{
const char *client_id = "org.tizen.some_service";
diagnostics_data_h data;
const char *params[] = {"custom_parameter"};
int ret = diagnostics_request_client_data(client_id, params, 1, &data);
if (ret != DIAGNOSTICS_ERROR_NONE)
return;
char buff[0x1000];
int timeout_ms = 0;
size_t bytes_read;
for (;;) {
ret = diagnostics_data_read(data, buff, sizeof(buff), timeout_ms, &bytes_read);
if (ret == DIAGNOSTICS_ERROR_TRY_AGAIN)
continue;
if (ret != DIAGNOSTICS_ERROR_NONE)
break; // error occurred
if (bytes_read == 0)
break; // no more data to read
fwrite(buff, 1, bytes_read, stdout); // write received data to the STDOUT
}
}
If diagnostics_request_client_data() returns successfully, the obtained data can be read by diagnostics_data_read().
Sometimes there is a need for getting data related to some specific diagnostics event. For example, Bugreport service sends an event that a new bug report has been created and the client wants to get the bug report’s content after receiving the event. If the application supports event-specific data request, then diagnostics_get_data() must be used.
Current implementations
Bugreport service
Bugreport service provides a diagnostic interface to allow you to read the bug reports in case the process in the system fails. To do so, you must register the callback diagnostics_set_notification_cb, it is called when the bug report is created:
void notification_handler(diagnostics_ctx_h ctx, void *user_data)
{
....
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
diagnostics_set_notification_cb(notification_handler, NULL);
diagnostics_subscribe_event("BugreportCreated", "org.tizen.bugreport-service");
}
To deregister the callback, use diagnostics_unset_notification_cb().
In case a new bug report is created, callback is called. To read the content of the bug report use diagnostics_get_data():
void notification_handler(diagnostics_ctx_h ctx, void *user_data)
{
diagnostics_data_h data;
const char *params[] = {"--type", "crash-info-json"};
diagnostics_get_data(ctx, params, 2, &data);
...
diagnostics_destroy(ctx);
}
Use the param argument to specify which data to read from the bug report. Currently, the proper values are:
--type <report_type>- Specify the report type. Available types are:"bugreport"- Bugreport file is returned, which contains information about system such as system logs, list of processes, and so on. The output can be modified by dump_systemstate configuration (default)."crash-info"- Returned report contains information about crashed process such as callstack, mapped memory regions, and so on."crash-info-json"- crash-info report in JSON format."fullreport"- Full crash report ZIP archive is collected (if single report specified)."coredumptar"- Coredump file in TAR archive (if single report specified).
--last <seconds>- Get reports generated within the last<seconds>.--from <timestamp>- Get reports generated after specified time.--to <timestamp>- Get reports generated before specified time (default: current time).<report_ident>- Get one specific report.
The obtained data is associated with the data Diagnostics handler. To read the data content, use diagnostics_data_read():
void notification_handler(diagnostics_ctx_h ctx, void *user_data)
{
diagnostics_data_h data;
const char *params[] = {"--type", "fullreport"};
int ret = diagnostics_get_data(ctx, params, 2, &data);
if (ret != DIAGNOSTICS_ERROR_NONE) {
diagnostics_destroy(ctx);
return;
}
char buff[0x1000];
int timeout_ms = 0;
size_t bytes_read;
for (;;) {
ret = diagnostics_data_read(data, buff, sizeof(buff), timeout_ms, &bytes_read);
if (ret == DIAGNOSTICS_ERROR_TRY_AGAIN)
continue;
if (ret != DIAGNOSTICS_ERROR_NONE)
break; // error occurred
if (bytes_read == 0)
break; // no more data to read
fwrite(buff, 1, bytes_read, stdout); // write received data to the STDOUT
}
diagnostics_destroy(ctx);
}
Stability monitor
Stability monitor provides interface org.tizen.stability-monitor for getting process-specific data such as:
- cpu usage
- memory usage
- io usage
- number of open file descriptors
The following example shows how to get data for the process of pid 1234, collected within last 5 seconds:
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
diagnostics_data_h data;
const char *params[] = {"--pid", "1234", "--last", "5"};
char buf[1000];
size_t bytes_read;
diagnostics_request_client_data("org.tizen.stability-monitor", params, sizeof(params)/sizeof(char*), &data);
while (true) {
diagnostics_data_read(data, buf, sizeof(buf)/sizeof(char), -1, &bytes_read);
if (bytes_read == 0) // Reached EOF
break;
// Process the chunk of data
}
diagnostics_data_destroy(data);
}
Supported parameters:
--pid <number>- dump only process with given pid,--type <module>- dump only specified module, ex.cpu,mem,io, orfd,--last <sec>- dump data from last<sec>seconds,--help- dump help message.
Additionally, stability monitor sends diagnostic event AbnormalityDetected in case of any of the monitored parameters exceed their limit set in the configuration.
Related information
- Dependencies
- Since Tizen 6.0
- API References