Smart Card
NoteAll Smart Card APIs have been deprecated since Tizen 10.0 and will be removed after two releases without any alternatives.
Tizen enables you to use smart card functionalities, such as accessing a secure element (SE). Before using the Smartcard API, make sure you have a secure element in the device. The smart card service allows you to open a session on an SE, open a channel to the applet in the SE, send a command to the channel, and finally receive a response to the command.
The main components of the Smartcard API include:
-
SE service
The SE Service API allows you to initialize and deinitialize the smart card features, and get the available readers. The SE service functions as a connector to the SE framework system.
-
Reader
The Reader API allows you to access the SE connected with the selected reader. You can get the reader name and open and close sessions.
-
Session
A session is an open connection between an application on the device and a SE. The Session API allows you to open and close basic and logical channels, and get ATR (answer to reset).
-
Channel
A channel is an open connection between an application on the device and an applet on the SE. The Channel API allows you to close channels and transmit application protocol data units (APDU).
All of the above are used when you send a transmission.
The following figure illustrates the smart card service architecture in Tizen. The smart card service sends and receives data through the terminal of each SE.
Figure: Smart card service architecture
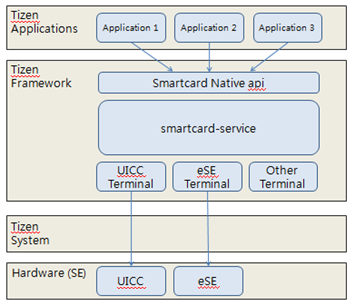
The Smartcard API is a reference implementation of the SIMalliance Open Mobile 3.0 API specification that enables Tizen applications to communicate with secure elements. For more information, see the SimAlliance. The Tizen implementation differs from the original as follows:
- Only the transport layer is provided. There is no service layer support in Tizen.
- The “get version” function does not exist. In Tizen, version management is not performed through a function.
- Allocation style differs dramatically. The Open Mobile API can facilitate the memory management by calling the API twice (for an example, see section 6.3.1, Usage pattern, in the SIMalliance Open Mobile 3.0 API specification). However, Tizen Smartcard API does not follow this allocation style.
- For the
SE Serviceobject management, Tizen provides functions for initialization and deinitialization.
Note
On some Tizen devices, after a specified time, the screen is automatically switched off and the CPU goes to the resting state. If this occurs during communication with the SE using the Smartcard API, the API may not function normally.
To avoid the screen switching off and the CPU going to the resting state, use the Device API to lock the device CPU (not the display):
#include <nfc.h> #include <device/power.h> device_power_request_lock(POWER_LOCK_CPU, 300000); /* Input your Smartcard API code */ device_power_release_lock(POWER_LOCK_CPU);
Prerequisites
To enable your application to use the smart card functionality:
-
To use the Smartcard API, the application has to request permission by adding the following privilege to the
tizen-manifest.xmlfile:<privileges> <privilege>http://tizen.org/privilege/secureelement</privilege> </privileges> -
To use the functions and data types of the Smartcard API, include the
<smartcard.h>header file in your application:#include <smartcard.h>
Using the SE Service
To use the SE service:
-
Initialize the smart card service for use:
int ret; ret = smartcard_initialize(); if (ret == SMARTCARD_ERROR_NONE) dlog_print(DLOG_INFO, LOG_TAG, "smartcard initialize successful"); else dlog_print(DLOG_INFO, LOG_TAG, "smartcard initialize failed");When the service is no longer needed, deinitialize it:
ret = smartcard_deinitialize(); if (ret == SMARTCARD_ERROR_NONE) dlog_print(DLOG_INFO, LOG_TAG, "smartcard deinitialize successful"); else dlog_print(DLOG_INFO, LOG_TAG, "smartcard deinitialize failed"); -
Retrieve the available readers with the
smartcard_get_readers()function:int pLength; int *phReaders = NULL; ret = smartcard_get_readers(&phReaders, &pLength); if (ret == SMARTCARD_ERROR_NONE) { dlog_print(DLOG_INFO, LOG_TAG, "smartcard_get_readers successful"); dlog_print(DLOG_INFO, LOG_TAG, "readers length: %d", pLength); } else { dlog_print(DLOG_INFO, LOG_TAG, "smartcard_get_readers failed: %d", ret); } if (phReaders != NULL) free(phReaders);
Managing the Reader
To manage a reader:
-
Retrieve the name of the reader with the
smartcard_reader_get_name()function:int ret; int reader = phReaders[0]; /* Get the reader using smartcard_get_readers() */ char * pReader = NULL; ret = smartcard_reader_get_name(reader, &pReader); if (ret == SMARTCARD_ERROR_NONE) { dlog_print(DLOG_INFO, LOG_TAG, "smartcard_reader_get_name successful"); dlog_print(DLOG_INFO, LOG_TAG, "reader name: %s", pReader); } else { dlog_print(DLOG_INFO, LOG_TAG, "smartcard_reader_get_name failed: %d", ret); } -
Before establishing a session, use the
smartcard_reader_is_secure_element_present()function to make sure that the SE is present in the reader:bool is_present = false; ret = smartcard_reader_is_secure_element_present(reader, &is_present); if (ret == SMARTCARD_ERROR_NONE) { dlog_print(DLOG_INFO, LOG_TAG, "smartcard_reader_is_secure_element_present successful"); dlog_print(DLOG_INFO, LOG_TAG, "reader secure element present: %d", is_present); } else { dlog_print(DLOG_INFO, LOG_TAG, "smartcard_reader_is_secure_element_present failed: %d", ret); } -
Open a session to connect to the SE in the reader using the
smartcard_reader_open_session()function.When you no longer need the reader, use the
smartcard_reader_close_sessions()function to close all sessions opened on the specific reader.int session; ret = smartcard_reader_open_session(reader, &session); if (ret == SMARTCARD_ERROR_NONE) { ret = smartcard_reader_close_sessions(reader); if (ret == SMARTCARD_ERROR_NONE) dlog_print(DLOG_INFO, LOG_TAG, "smartcard_reader_close_sessions successful"); else dlog_print(DLOG_INFO, LOG_TAG, "smartcard_reader_close_sessions failed: %d", ret); } else { dlog_print(DLOG_INFO, LOG_TAG, "open session failed: %d", ret); }
Managing Sessions
You can manage a session using the session instance that you have created when opening the session with a reader. The session instance is the first parameter in all session-related APIs.
To manage sessions:
-
Retrieve the reader that provides the session:
int ret; int reader; ret = smartcard_session_get_reader(session, &reader); ret = smartcard_reader_get_name(reader, &pReader); if (ret == SMARTCARD_ERROR_NONE) { dlog_print(DLOG_INFO, LOG_TAG, "smartcard_session_get_reader successful"); dlog_print(DLOG_INFO, LOG_TAG, "reader name: %s", pReader); } else { dlog_print(DLOG_INFO, LOG_TAG, "smartcard_session_get_reader failed"); } -
Retrieve the answer to reset (ATR) of the SE:
int i; int ret; unsigned char *pAtr; int pLength; ret = smartcard_session_get_atr(session, &pAtr, &pLength); if (ret == SMARTCARD_ERROR_NONE) { dlog_print(DLOG_INFO, LOG_TAG, "smartcard_session_get_atr successful: %d", pLength); for (i = 0; i < pLength; i++) dlog_print(DLOG_INFO, LOG_TAG, "%x ", (int)pAtr[i]); } else { dlog_print(DLOG_INFO, LOG_TAG, "smartcard_session_get_atr failed"); } -
Open a basic or logical channel.
A basic channel is defined in the ISO/IEC 7816-4 specification (the one that has number 0). To open a logical channel with the SE, you must select the applet represented by the given Application ID (AID).
int ret; unsigned char aid[] = {0x00, 0x01, 0x02, 0x03}; int channel; /* Open basic channel */ ret = smartcard_session_open_basic_channel(session, aid, 4, 0x00, &channel); if (ret == SMARTCARD_ERROR_NONE) dlog_print(DLOG_INFO, LOG_TAG, "smartcard_session_open_basic_channel successful: %d", channel); else dlog_print(DLOG_INFO, LOG_TAG, "smartcard_session_open_basic_channel failed"); /* Open logical channel */ ret = smartcard_session_open_logical_channel(session, aid, 12, 0x04, &channel); if (ret == SMARTCARD_ERROR_NONE) dlog_print(DLOG_INFO, LOG_TAG, "smartcard_session_open_logical_channel successful: %d", (channel); else dlog_print(DLOG_INFO, LOG_TAG, "smartcard_session_open_logical_channel failed: %d", ret); -
Close all channels opened for a specific session:
int ret; ret = smartcard_session_close_channels(session); if (ret == SMARTCARD_ERROR_NONE) dlog_print(DLOG_INFO, LOG_TAG, "smartcard_session_close_channels successful"); else dlog_print(DLOG_INFO, LOG_TAG, "smartcard_session_close_channels failed"); -
Close a session and check that it is truly closed:
int ret; bool is_closed; ret = smartcard_session_close(session); if (ret == SMARTCARD_ERROR_NONE) dlog_print(DLOG_INFO, LOG_TAG, "smartcard_session_close successful"); else dlog_print(DLOG_INFO, LOG_TAG, "smartcard_session_close failed"); ret = smartcard_session_is_closed(session, &is_closed); if (ret == SMARTCARD_ERROR_NONE && is_closed == true) dlog_print(DLOG_INFO, LOG_TAG, "smartcard_session_is_closed successful"); else dlog_print(DLOG_INFO, LOG_TAG, "smartcard_session_is_closed failed");
Managing Channels
You can manage a channel using the channel instance that you have created when opening the channel with a session. The channel instance is the first parameter in all channel-related APIs.
To manage channels:
-
Retrieve the session that has opened the specific channel:
int ret; int session_handle; ret = smartcard_session_open_logical_channel(session, aid, 12, 0x00, &channel); if (ret == SMARTCARD_ERROR_NONE) { ret = smartcard_channel_get_session(channel, &session_handle); if (ret == SMARTCARD_ERROR_NONE) dlog_print(DLOG_INFO, LOG_TAG, "smartcard_channel_get_session successful: %d", session_handle); else dlog_print(DLOG_INFO, LOG_TAG, "smartcard_channel_get_session failed"); } -
Check whether a specific channel is a basic or logical channel:
int ret; bool is_basic; ret = smartcard_channel_is_basic_channel(channel, &is_basic); if (ret == SMARTCARD_ERROR_NONE && is_basic == false) dlog_print(DLOG_INFO, LOG_TAG, "smartcard_channel_is_basic_channel successful"); else dlog_print(DLOG_INFO, LOG_TAG, "smartcard_channel_is_basic_channel failed"); -
Select the next applet on the specific channel that matches to the partial Application ID (AID):
ret = smartcard_session_open_logical_channel(session, aid, 12, 0x00, &channel); if (ret == SMARTCARD_ERROR_NONE) { bool is_next = true; ret = smartcard_channel_select_next(channel, &is_next); if (ret == SMARTCARD_ERROR_NONE && is_next == false) dlog_print(DLOG_INFO, LOG_TAG, "smartcard_channel_select_next successful"); else dlog_print(DLOG_INFO, LOG_TAG, "smartcard_channel_select_next failed"); }To get a response for the selection command, use the
smartcard_channel_get_select_response()function:int i; int ret; unsigned char* pSelectResponse; int pLength; ret = smartcard_channel_get_select_response(channel, &pSelectResponse, &pLength); if (ret == SMARTCARD_ERROR_NONE) { dlog_print(DLOG_INFO, LOG_TAG, "smartcard_channel_get_select_response successful"); for (i = 0; i < pLength; i++) g_print("%x ", (int)pSelectResponse[i]); } else { dlog_print(DLOG_INFO, LOG_TAG, "smartcard_channel_get_select_response failed"); } -
Check whether a specific channel is closed:
int ret; bool is_close; ret = smartcard_channel_close(channel); ret = smartcard_channel_is_closed(channel, &is_close); if (ret == SMARTCARD_ERROR_NONE && is_close == true) dlog_print(DLOG_INFO, LOG_TAG, "smartcard_channel_is_closed successful"); else dlog_print(DLOG_INFO, LOG_TAG, "smartcard_channel_is_closed failed"); -
Close the channel opened for a specific SE:
int ret; ret = smartcard_channel_close(channel); if (ret == SMARTCARD_ERROR_NONE) dlog_print(DLOG_INFO, LOG_TAG, "smartcard_channel_close successful"); else dlog_print(DLOG_INFO, LOG_TAG, "smartcard_channel_close failed: %d", ret); -
Transmit an APDU command (as per ISO/IEC 7816-4) to the SE:
int i; int ret; int resp_len; unsigned char *response = NULL; unsigned char command[] = {0x00, 0x01, 0x02, 0x03}; ret = smartcard_channel_transmit(channel, command, 4, &response, &resp_len); if (ret == SMARTCARD_ERROR_NONE) { dlog_print(DLOG_INFO, LOG_TAG, "smartcard_channel_transmit successful"); dlog_print(DLOG_INFO, LOG_TAG, "response is "); for (i = 0; i < resp_len; i++) dlog_print(DLOG_INFO, LOG_TAG, "%x ", (int)response[i]); dlog_print(DLOG_INFO, LOG_TAG, "\n"); } else { dlog_print(DLOG_INFO, LOG_TAG, "smartcard_channel_transmit failed"); }To get a response for the transmission, use the
smartcard_channel_transmit_retrieve_response()function:int i; unsigned char * ptransmitResponse; ret = smartcard_session_open_logical_channel(session, aid, 12, 0x00, &channel); if (ret == SMARTCARD_ERROR_NONE) { ret = smartcard_channel_transmit(channel, command, 11, &response, &resp_len); ret = smartcard_channel_transmit_retrieve_response(channel, &ptransmitResponse, &pLength); if (ret == SMARTCARD_ERROR_NONE) { dlog_print(DLOG_INFO, LOG_TAG, "smartcard_channel_transmit_get_response successful"); dlog_print(DLOG_INFO, LOG_TAG, "response is "); for (i = 0; i < pLength; i++) dlog_print(DLOG_INFO, LOG_TAG, "%x ", (int)ptransmitResponse[i]); dlog_print(DLOG_INFO, LOG_TAG, "\n"); } else { dlog_print(DLOG_INFO, LOG_TAG, "smartcard_channel_transmit_get_response failed"); } }
Sending a Transmission
This use case covers the entire work flow of sending an APDU transmission from getting a reader to closing the session afterwards.
To send a transmission:
-
Define the required variables and initialize the smart card service for use:
int i = 0; int pLength; int *phReaders = NULL; int session; int channel; unsigned char aid[] = {0xA0, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x63, 0x50, 0x4B, 0x43, 0x53, 0x2D, 0x31, 0x35}; unsigned char command[] = {0x00, 0x28, 0x00, 0x00}; unsigned char *response = NULL; int resp_len = 50; ret = smartcard_initialize(); if (ret == SMARTCARD_ERROR_NONE) dlog_print(DLOG_INFO, LOG_TAG, "smartcard initialize successful"); else dlog_print(DLOG_INFO, LOG_TAG, "smartcard initialize failed"); -
Get the available readers:
ret = smartcard_get_readers(&phReaders, &pLength); -
Open a session:
if (ret == SMARTCARD_ERROR_NONE && pLength != 0) { ret = smartcard_reader_open_session(phReaders[0], &session); -
Open a logical channel:
if (ret == SMARTCARD_ERROR_NONE && session != 0) { ret = smartcard_session_open_logical_channel(session, aid, 12, 0x00, &channel); -
Transmit the command:
if (ret == SMARTCARD_ERROR_NONE) { ret = smartcard_channel_transmit(channel, command, 4, &response, &resp_len); if (ret == SMARTCARD_ERROR_NONE) { dlog_print(DLOG_INFO, LOG_TAG, "smartcard_channel_transmit successful"); dlog_print(DLOG_INFO, LOG_TAG, "response is "); for (i = 0; i < resp_len; i++) dlog_print(DLOG_INFO, LOG_TAG, "%x ", (int)response[i]); dlog_print(DLOG_INFO, LOG_TAG, "\n"); } else { dlog_print(DLOG_INFO, LOG_TAG, "smartcard_channel_transmit failed"); } } } -
Close the session:
ret = smartcard_session_close(session); } -
Deinitialize the service:
ret = smartcard_deinitialize(); if (ret == SMARTCARD_ERROR_NONE) dlog_print(DLOG_INFO, LOG_TAG, "smartcard deinitialize successful"); else dlog_print(DLOG_INFO, LOG_TAG, "smartcard deinitialize failed");
Related information
- Dependencies
- Since Tizen 2.4
- API References