Message Port
Tizen applications can communicate with each other using message ports. Applications can send and receive messages through message port communication. The message data type for communication is a map data which consists of a bundle (key and value pair).
The main features of the Tizen.Applications.Messages.MessagePort and Tizen.Applications.Messages.RemotePort classes include the following:
-
Managing a message port
You can set up message ports to send and receive messages between applications with the
Tizen.Applications.Messages.MessagePortclass.An application needs to register its local port to receive messages from remote applications.
-
Managing a remote port
You can verify that a remote port is running with the
Tizen.Applications.Messages.RemotePortclass and to receive events about the registration status of the remote port. -
Using trusted communication
You can set message ports or remote ports as trusted, which restricts communication through them to applications that share a signing certificate.
Prerequisites
To enable your application to use the message port functionality, follow these steps:
-
You need 2 applications to communicate with each other through the message port.
-
To use trusted message port communication, both applications must have the same certificate. To create and register an author certificate, go to the Visual Studio menu and select Tools > Tizen > Certificate Manager. For more information, see Certificate Manager.
-
To use the methods and properties of the Tizen.Applications.Messages.MessagePort and Tizen.Applications.Messages.RemotePort classes, include the Tizen.Applications.Messages namespace in your application:
C#Copyusing Tizen.Applications.Messages;
Manage a message port
To send a message from one application (LocPortApp.Tizen) to another (RmtPortApp.Tizen) using the Tizen.Applications.Messages.MessagePort class, follow these steps:
-
Create a message port instance in each application.
In the sending application (
LocPortApp.Tizen):C#Copynamespace LocPortApp.Tizen { class App : NUIApplication { private static MessagePort _msgPort; private string TAG; protected override void OnTerminate() { base.OnTerminate(); Log.Debug(TAG, "Terminate"); } protected override void OnCreate() { base.OnCreate(); TAG = "LOCALMSGPORTAPP"; Log.Debug(TAG, "Create"); _msgPort = new MessagePort("my_port", false); Log.Debug(TAG, "MessagePort Create: " + _msgPort.PortName + "Trusted: " + _msgPort.Trusted); } }In the receiving application (
RmtPortApp.Tizen):C#Copynamespace RmtPortApp.Tizen { class App : NUIApplication { private static MessagePort _rmtPort; private string TAG; protected override void OnTerminate() { base.OnTerminate(); Log.Debug(TAG, "Terminate"); } protected override void OnCreate() { base.OnCreate(); Initialize(); TAG = "REMOTEMSGPORTAPP"; Log.Debug(TAG, "Create"); _rmtPort = new MessagePort("my_port", false); Log.Debug(TAG, "MessagePort Create: " + _rmtPort.PortName + "Trusted: " + _rmtPort.Trusted); } } -
Set up the receiving application.
To have the receiving application listen for incoming messages, call the
Listen()method of theTizen.Applications.Messages.MessagePortclass.To handle the received message, define and register an event handler for the
MessageReceivedevent of theTizen.Applications.Messages.MessagePortclass:C#Copy{ _rmtPort.MessageReceived += MessageReceived_Callback; _rmtPort.Listen(); } private void MessageReceived_Callback(object sender, MessageReceivedEventArgs e) { Log.Debug(TAG, "Message Received"); Log.Debug(TAG, "App ID: " + e.Remote.AppId); Log.Debug(TAG, "PortName: " + e.Remote.PortName); Log.Debug(TAG, "Trusted: " + e.Remote.Trusted); Log.Debug(TAG, "message: " + e.Message.GetItem <string> ("message")); } -
In the sending application, to send the message, follow these steps:
a. You must register to a local port.
b. Call the
Listen()methodTizen.Applications.Messages.MessagePortclass.c. Use
Send()methodTizen.Applications.Messages.MessagePortclass to send the message.d. Provide the message to be sent as an instance of the Tizen.Applications.Bundle class as shown in the code below:
C#Copystring remoteAppId = "RmtPortApp.Tizen"; string remotePort = "my_port"; _msgPort.Listen(); var msg = new Bundle(); msg.AddItem("message", "Send_A_MESSAGE_TO_A_REMOTE_APP"); _msgPort.Send(msg, remoteAppId, remotePort); Log.Debug(LogTag, "send !! ");
Figure: Message port communication
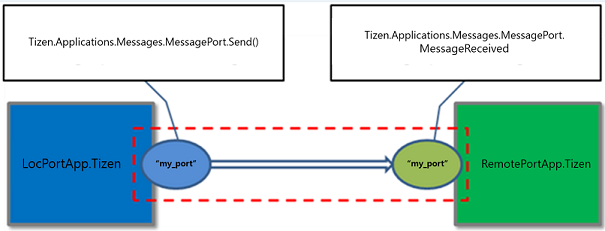
Manage a remote port
By using Tizen.Applications.Messages.RemotePort class, an application can check whether the message port in another application is running and be notified if the state changes.
To check whether the receiving application (RmtPortApp.Tizen) is running and receive notifications about the registration status of the remote port, follow these steps:
-
Create the remote port instance in the sending application (
LocPortApp.Tizen):C#Copynamespace LocPortApp.Tizen { class App : NUIApplication { private static RemotePort _remotePort; private const string PortName = "my_port"; private const string MyRemoteAppId = "RmtPortApp.Tizen"; private string TAG; protected override void OnTerminate() { base.OnTerminate(); Log.Debug(TAG, "Terminate"); } protected override void OnCreate() { base.OnCreate(); TAG = "LOCALMSGPORTAPP"; Log.Debug(TAG, "Create"); _remotePort = new RemotePort(MyRemoteAppId, PortName, false); Log.Debug(TAG, "RemotePort Create: " + _remotePort.AppId + _remotePort.PortName + "Trusted: " + _remotePort.Trusted); } } } -
To check whether a remote port is running, use the
IsRunningproperty of theTizen.Applications.Messages.RemotePortinstance:C#Copybool isRunning = false; isRunning = _remotePort.IsRunning(); Log.Debug(TAG, "RmtPortApp.Tizen is running: " + isRunning); -
To receive events about the registration status of the remote port, register an event handler for the
RemotePortStateChangedevent of theTizen.Applications.Messages.RemotePortclass.When the
RmtPortApp.Tizenapplication is registered, it triggers the event handler in theLocPortApp.Tizenapplication:C#Copy_remotePort.RemotePortStateChanged += RemotePortStateChanged; static void RemotePortStateChanged(object sender, RemotePortStateChangedEventArgs e) { switch (e.Status) { case State.Registered: Log.Debug(LogTag, "remote port is registered"); _flag_registered = true; break; case State.Unregistered: Log.Debug(LogTag, "remote port is unregistered"); _flag_unregistered = true; break; default: break; } }
Use trusted communication
You can set an instance of the Tizen.Applications.Messages.MessagePort or Tizen.Applications.Messages.RemotePort class as a trusted message port by setting its Trusted property as true. Communication is only allowed over a trusted message port if both applications are signed with a certificate that is uniquely assigned to its developer.
Related information
- Dependencies
- Tizen 4.0 and Higher
- API References