Geofences
NoteAll geofence APIs have been deprecated since Tizen 8.0 and will be removed after two releases without any alternatives.
A geofence is a virtual perimeter for a real-world geographic area. A geofence is defined by either a geopoint and radius for geopoint geofences or by a MAC address for Wi-Fi and Bluetooth geofences. The geofence feature alerts the user when the geofence state changes (the user crosses the perimeter).
The main features of the Tizen.Location.Geofence namespace include the following:
-
Using the geofence service
You can use the geofence service to create different types of geofences and retrieve information about them, get the geofence event state, and track the user for alerts.
-
Defining a geofence
You can define the type of the geofence when creating one.
-
Managing the geofence service
You can allow the user to manage the geofence places and fences through the My Places application.
Figure: Geofence architecture
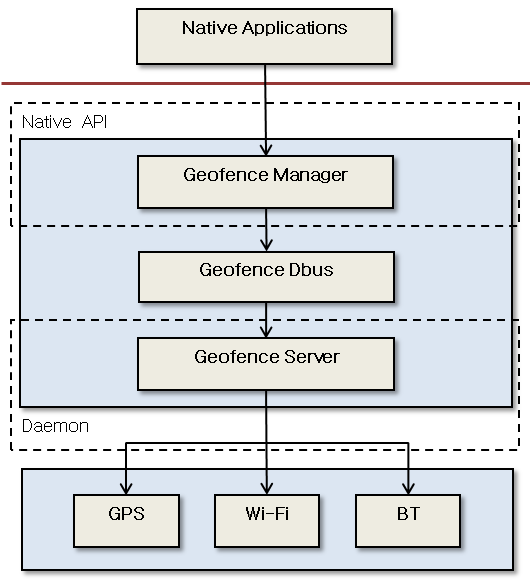
Geofence service
With the geofence service, you can do the following:
-
Get in and out alerts and proximity alerts
You can get notifications when the user approaches or crosses any geofences they have defined.
-
Retrieve information about created geofences
The device can receive alerts about the geofence when a particular geofence service is started using the
Start()method of the Tizen.Location.Geofence.GeofenceManager class.If the user revokes permission to use the location information, an
UnauthorizedAccessExceptionis returned to the application attempting to use the geofence service.Asynchronous geofence-related alerts (in or out) and event handling (a fence added or removed) are implemented with event handlers. Geofence alerts are received using the values of the Tizen.Location.Geofence.GeofenceState enumeration.
Geofence definition
Geofence definition refers to defining an instance of the Tizen.Location.Geofence.Fence class.
The 3 types of available geofences are geopoint, Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth. When creating the geofence, define the type using the values of the Tizen.Location.Geofence.FenceType enumeration.
Creating a geopoint geofence requires a geopoint and a radius, whereas Wi-Fi and Bluetooth geofences require a MAC address. Based on the defined geofence type, the geofence manager creates the fence for the particular application.
Geofence management through My Places
Tizen provides the user with a way of managing geofence places and fences through the My Places application. The following figure shows the default places and supported fence types.
Figure: My Places
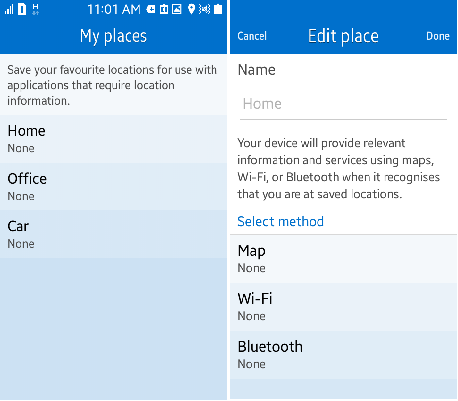
My Places controls the adding, removing, and updating of places and fences. Home, Office, and Car are the default places. Map, Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth are the supported fence methods. Car supports only Wi-Fi and Bluetooth as fence methods.
Prerequisites
To use the methods and properties of the Tizen.Location.Geofence namespace, include it in your application:
C#
Copy
using Tizen.Location.Geofence;
Start the geofence service
To start the geofence service, follow these steps:
-
Create a Tizen.Location.Geofence.GeofenceManager object:
C#CopyGeofenceManager manager = new GeofenceManager();Each geofence manager is an independent service. The event handlers are set for a given geofence manager and are called only if the service is started by their manager.
-
Create a place to be used for the geofences:
C#CopyVirtualPerimeter perimeter = new VirtualPerimeter(manager); int placeId = perimeter.AddPlaceName("Place");Note
A place is used to accommodate a number of geofences and is identified by a place ID. Each place can have a name. A geofence is identified by a geofence ID.
-
Create the geofences you need:
-
Geopoint geofence:
C#Copydouble latitude = 12.756738; double longitude = 77.386474; int radius = 100; char* address = "India"; Fence fence = Fence.CreateGPSFence(placeId, latitude, longitude, radius, address); -
Bluetooth geofence:
C#Copychar* bssid = "82:45:67:7E:4A:3B"; char* ssid = "Cafeteria"; Fence fence = Fence.CreateBTFence(place_id, bssid, ssid);
-
-
Add the geofence to the geofence manager:
C#Copyint geofenceId = perimeter.AddGeofence(fence); -
Start the geofence service using the
Start()method of theTizen.Location.Geofence.GeofenceManagerclass.This call is asynchronous and only initiates the process of starting the service. Once the service is started, the added event handlers are invoked when their corresponding events take place. To know when the service becomes enabled, use the
StateChangedevent of theTizen.Location.Geofence.GeofenceManagerclass:C#Copymanager.Start(geofenceId); -
Using the geofence service for geopoints adds to power consumption, so if the service is not used, stop the status alerts using the
Stop()method of theTizen.Location.Geofence.GeofenceManagerclass. Call theStart()method again if the alerts are needed:C#Copymanager.Stop(geofenceId); -
Destroy all used resources using the
Dispose()method of theTizen.Location.Geofence.GeofenceManagerclass:C#Copymanager.Dispose(); manager = NULL;If you destroy the
Tizen.Location.Geofence.GeofenceManagerinstance, there is no need to call theStop()method to stop the service, as the service is automatically stopped.
Monitor geofence state changes
To track the state of the geofence, use the GeofenceEventChanged event of the Tizen.Location.Geofence.GeofenceManager class. An event handler is invoked whenever there is a request from the user, such as to add a geofence or to start a geofence service.
-
Add the event handler for the
GeofenceEventChangedevent:C#Copymanager.GeofenceEventChanged += handler; -
Get the success or failure state of the event in the handler:
C#CopyEventHandler<GeofenceResponseEventArgs> handler = (object sender, GeofenceResponseEventArgs args) => { placeId = args.PlaceId; FenceId = args.FenceId; errorCode = args.ErrorCode; eventType = args.EventType; };Note
The geofence change event handler is used to let the user know whether the request is successful on the server side. This handler is invoked only in the case of an asynchronous method. For a synchronous method, an error is immediately returned.
Track the user for geofence crossing alerts
To get information about whether the user has crossed the boundary of the geofence, follow these steps:
-
Receive event-based notifications with an event handler.
You can be notified when the user crosses a particular fence. The handler receives the current state of the user (whether the user is in or out of the virtual boundaries of a geofence) with each call.
-
Define the event handler:
C#CopyEventHandler<GeofenceStateEventArgs> handler = (object sender, GeofenceStateEventArgs args) => {}; -
Register the handler using the
StateChangedevent of theTizen.Location.Geofence.GeofenceManagerclass.C#Copymanager.StateChanged += handler;
-
-
Retrieve the current state on request.
You can get the current state of the user with respect to a geofence, such as their in or out state and the duration of the current state.
-
Create a Tizen.Location.Geofence.FenceStatus instance:
C#CopyFenceStatus status = new FenceStatus(fenceId); -
To get the current state and duration of that state, use the
StateandDurationproperties of theTizen.Location.Geofence.FenceStatusclass:C#CopyGeofenceState state = status.State; int duration = status.Duration;The duration is provided in seconds.
-
When no longer needed, destroy the
Tizen.Location.Geofence.FenceStatusinstance with theDispose()method:C#Copystatus.Dispose();
-
Track the user for proximity alerts
To get information about the user’s proximity to a geofence, use an event handler that receives the user’s proximity with each call:
-
Define the event handler:
C#CopyEventHandler<ProximityStateEventArgs> handler = (object sender, ProximityStateEventArgs args) => {}; -
Register the handler using the
ProximityChangedevent of theTizen.Location.Geofence.GeofenceManagerclass:C#Copymanager.ProximityChanged += handler;
Retrieve geofence information
To get information about a geofence, follow these steps:
-
Get common information (such as the type and place) about any type of geofence:
C#Copyint placeId = fence.PlaceId; Fence type = fence.Type; -
Get information specific to a geopoint geofence:
C#Copydouble latitude = fence.Latitude; double longitude = fence.Longitude; int radius = fence.Radius; string address = fence.Address; -
Get information specific to a Wi-Fi or Bluetooth geofence:
C#Copystring bssid = fence.Bssid; string ssid = fence.Ssid;
Related information
- Dependencies
- Tizen 4.0 and Higher